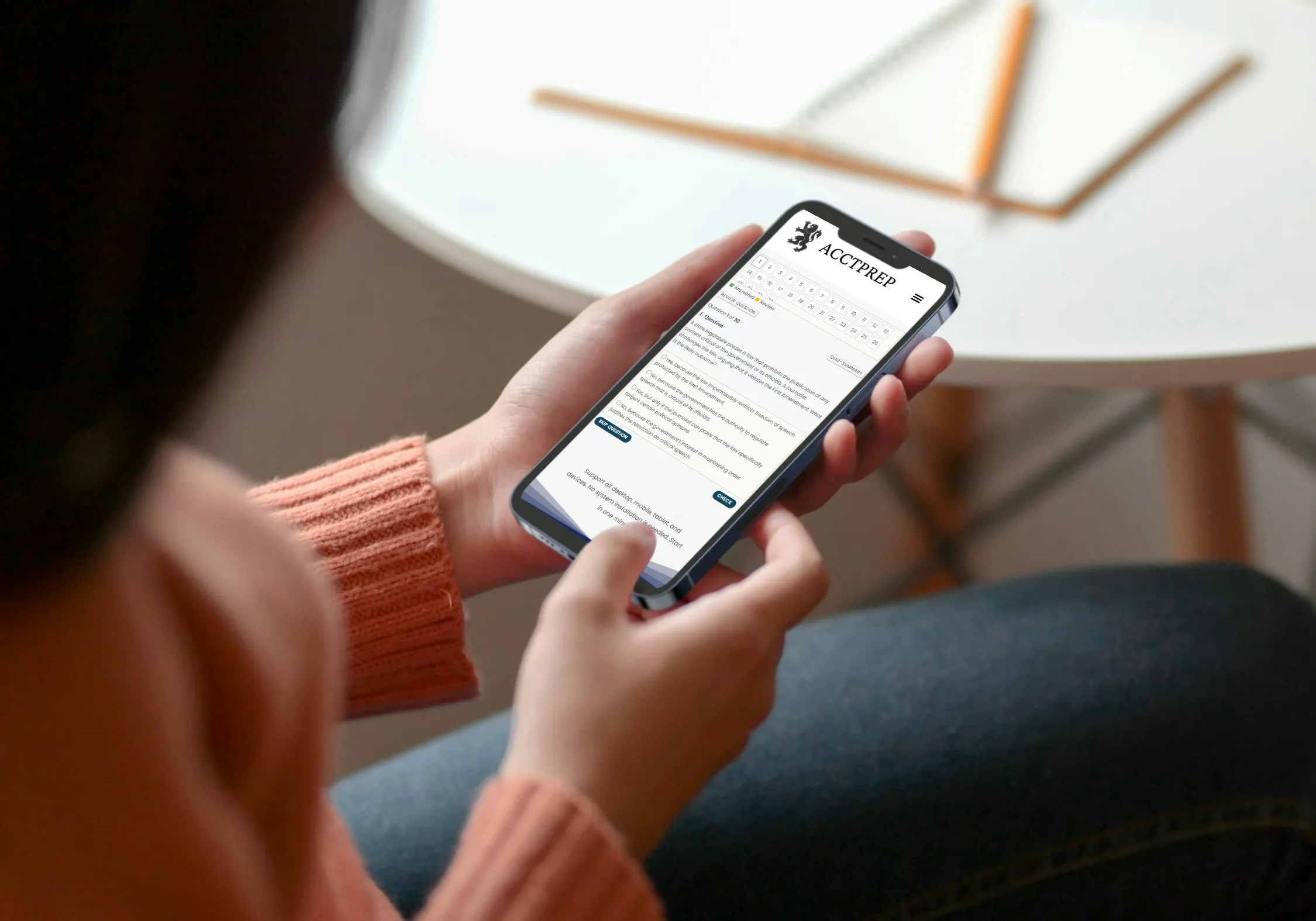
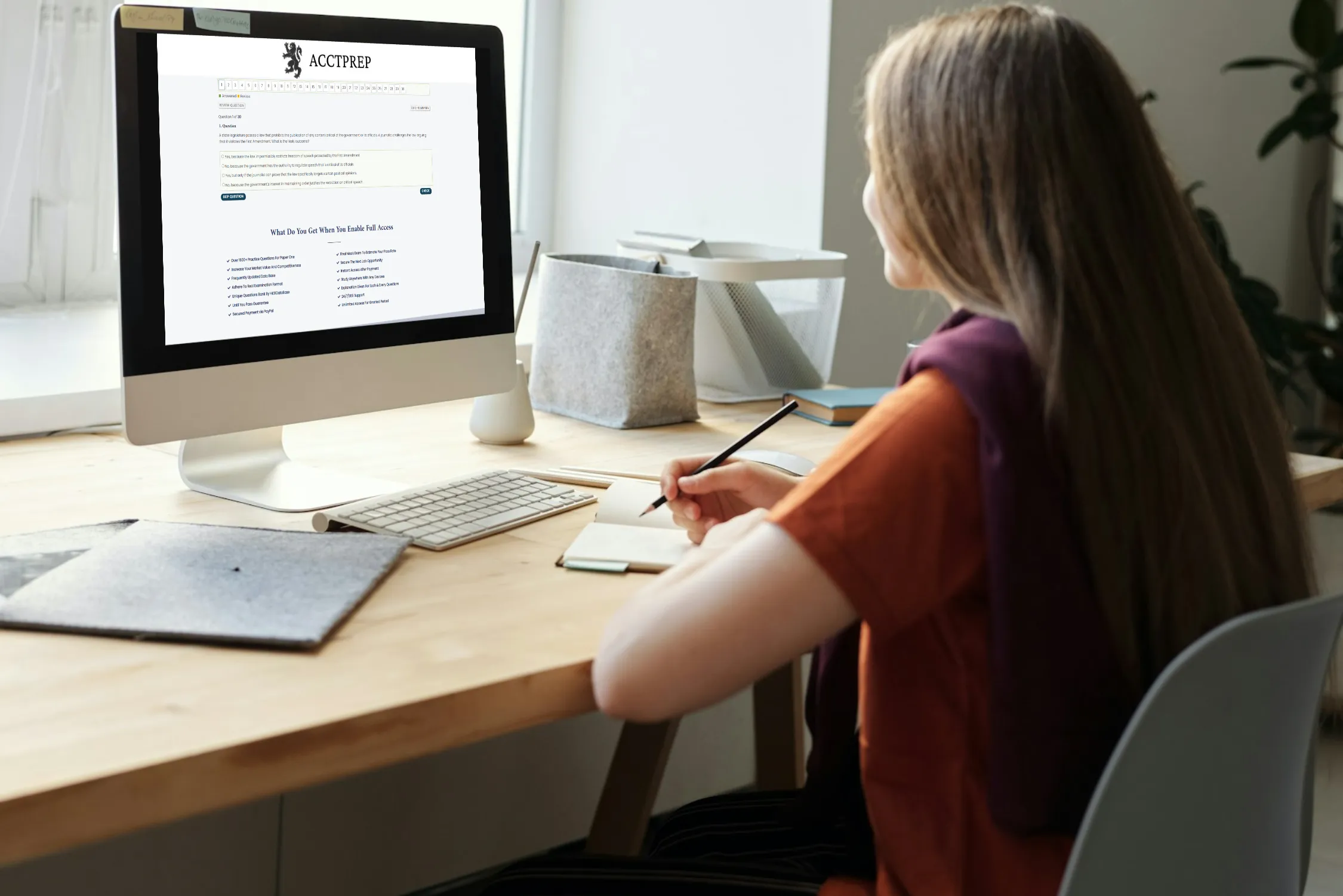
Quiz-summary
0 of 30 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Information
Premium Practice Questions
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
Results
0 of 30 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 30
1. Question
The assessment process reveals a significant data breach impacting client personal information. The IT security team has identified the initial point of compromise and is working on isolating the affected systems. What is the most appropriate immediate course of action for the organization’s cybersecurity leadership?
Correct
Scenario Analysis: This scenario is professionally challenging because it involves a critical cybersecurity incident that directly impacts client data and operational integrity. The pressure to respond quickly while ensuring compliance with regulatory obligations and maintaining client trust is immense. Professionals must balance immediate containment and remediation efforts with thorough investigation and reporting requirements, all within a dynamic and potentially evolving threat landscape. The need for clear communication, accurate documentation, and adherence to established protocols is paramount to mitigating further damage and legal repercussions. Correct Approach Analysis: The correct approach involves a structured, multi-phased incident response plan that prioritizes containment, eradication, and recovery, while simultaneously initiating forensic investigation and regulatory notification. This aligns with best practices and regulatory expectations for cybersecurity incident response. Specifically, it emphasizes immediate steps to limit the scope of the breach, followed by a systematic process to remove the threat, restore affected systems, and conduct a detailed analysis of the incident’s root cause and impact. Crucially, it includes timely and accurate reporting to relevant regulatory bodies and affected parties as mandated by law and ethical obligations. This comprehensive strategy ensures that the organization not only addresses the immediate crisis but also learns from the incident to improve its security posture and comply with its duties. Incorrect Approaches Analysis: Focusing solely on immediate system restoration without a proper forensic investigation is professionally unacceptable. This approach risks leaving the root cause unaddressed, allowing the threat to persist or re-emerge, and failing to gather crucial evidence required for regulatory reporting and legal proceedings. It also neglects the obligation to understand the full scope of the breach and the types of data compromised. Prioritizing public relations and client communication over containment and investigation is also a significant failure. While communication is important, it must be informed by accurate information derived from a proper incident response process. Premature or inaccurate communication can mislead stakeholders, damage reputation further, and create legal liabilities. It also suggests a misallocation of resources and priorities during a critical event. Delaying regulatory notification until the entire incident is resolved is a critical ethical and regulatory failure. Many jurisdictions have strict timelines for reporting cybersecurity incidents to authorities. Such a delay can result in significant penalties, loss of credibility, and a perception of non-compliance and a lack of transparency. It also deprives regulators of timely information that might help prevent similar incidents elsewhere. Professional Reasoning: Professionals facing a cybersecurity incident must adopt a systematic and compliant approach. This involves activating a pre-defined incident response plan, which typically includes phases for preparation, identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned. The decision-making process should be guided by the principle of minimizing harm to clients and the organization, while adhering strictly to all applicable laws and regulations. This means prioritizing actions that contain the threat, preserve evidence, and ensure timely and accurate reporting to all relevant parties, including regulatory bodies. A proactive and transparent approach, grounded in established protocols and ethical considerations, is essential for effective incident management and maintaining stakeholder trust.
Incorrect
Scenario Analysis: This scenario is professionally challenging because it involves a critical cybersecurity incident that directly impacts client data and operational integrity. The pressure to respond quickly while ensuring compliance with regulatory obligations and maintaining client trust is immense. Professionals must balance immediate containment and remediation efforts with thorough investigation and reporting requirements, all within a dynamic and potentially evolving threat landscape. The need for clear communication, accurate documentation, and adherence to established protocols is paramount to mitigating further damage and legal repercussions. Correct Approach Analysis: The correct approach involves a structured, multi-phased incident response plan that prioritizes containment, eradication, and recovery, while simultaneously initiating forensic investigation and regulatory notification. This aligns with best practices and regulatory expectations for cybersecurity incident response. Specifically, it emphasizes immediate steps to limit the scope of the breach, followed by a systematic process to remove the threat, restore affected systems, and conduct a detailed analysis of the incident’s root cause and impact. Crucially, it includes timely and accurate reporting to relevant regulatory bodies and affected parties as mandated by law and ethical obligations. This comprehensive strategy ensures that the organization not only addresses the immediate crisis but also learns from the incident to improve its security posture and comply with its duties. Incorrect Approaches Analysis: Focusing solely on immediate system restoration without a proper forensic investigation is professionally unacceptable. This approach risks leaving the root cause unaddressed, allowing the threat to persist or re-emerge, and failing to gather crucial evidence required for regulatory reporting and legal proceedings. It also neglects the obligation to understand the full scope of the breach and the types of data compromised. Prioritizing public relations and client communication over containment and investigation is also a significant failure. While communication is important, it must be informed by accurate information derived from a proper incident response process. Premature or inaccurate communication can mislead stakeholders, damage reputation further, and create legal liabilities. It also suggests a misallocation of resources and priorities during a critical event. Delaying regulatory notification until the entire incident is resolved is a critical ethical and regulatory failure. Many jurisdictions have strict timelines for reporting cybersecurity incidents to authorities. Such a delay can result in significant penalties, loss of credibility, and a perception of non-compliance and a lack of transparency. It also deprives regulators of timely information that might help prevent similar incidents elsewhere. Professional Reasoning: Professionals facing a cybersecurity incident must adopt a systematic and compliant approach. This involves activating a pre-defined incident response plan, which typically includes phases for preparation, identification, containment, eradication, recovery, and lessons learned. The decision-making process should be guided by the principle of minimizing harm to clients and the organization, while adhering strictly to all applicable laws and regulations. This means prioritizing actions that contain the threat, preserve evidence, and ensure timely and accurate reporting to all relevant parties, including regulatory bodies. A proactive and transparent approach, grounded in established protocols and ethical considerations, is essential for effective incident management and maintaining stakeholder trust.
-
Question 2 of 30
2. Question
The performance metrics show a consistent, minor deviation from a specific International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standard and Recommended Practice (SARP) related to air traffic control communication procedures. This deviation has not resulted in any reported safety incidents or operational disruptions. What is the most appropriate professional response to this situation?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires an aviation professional to balance operational efficiency with strict adherence to international aviation safety standards, specifically those set by ICAO. The core challenge lies in interpreting and applying ICAO Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) in a way that ensures safety without unduly hindering necessary operational adjustments. The professional must exercise sound judgment to determine when a deviation from a SARP is a minor, acceptable variance and when it constitutes a significant safety risk requiring immediate and formal action. The correct approach involves a thorough assessment of the deviation against the intent and safety objectives of the relevant ICAO SARPs. This means understanding not just the letter of the regulation but also its underlying purpose. If the deviation, even if minor in operational terms, compromises the safety assurance provided by the SARP, then it must be addressed through formal channels, potentially involving reporting, investigation, and corrective action. This aligns with the overarching ICAO objective of achieving a globally harmonized level of aviation safety. The justification for this approach is rooted in the principle of safety first, which is paramount in aviation and is the foundational principle of ICAO SARPs. An incorrect approach would be to dismiss the deviation as insignificant without a proper safety assessment. This failure stems from a lack of due diligence and an underestimation of the cumulative impact of minor deviations. Ethically and regulatorily, this is unacceptable as it bypasses established safety management processes and could lead to a gradual erosion of safety standards. Another incorrect approach is to immediately escalate the issue without first attempting to understand the context and potential impact of the deviation. While caution is important, an overreaction without proper analysis can lead to unnecessary administrative burdens and can undermine trust in the reporting and safety management system. It fails to demonstrate professional judgment in assessing the severity of the issue. Professionals should employ a structured decision-making process when encountering deviations from ICAO SARPs. This process should include: 1) Identifying the specific ICAO SARP that appears to be affected. 2) Understanding the purpose and safety intent of that SARP. 3) Assessing the nature and extent of the deviation. 4) Evaluating the potential safety impact of the deviation, considering both immediate and cumulative effects. 5) Determining if the deviation compromises the safety assurance provided by the SARP. 6) If a safety compromise is identified, initiating the appropriate reporting and corrective action procedures as mandated by the relevant State’s aviation authority and ICAO guidance. If no safety compromise is identified, documenting the deviation and the rationale for its acceptance for future reference and continuous improvement.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires an aviation professional to balance operational efficiency with strict adherence to international aviation safety standards, specifically those set by ICAO. The core challenge lies in interpreting and applying ICAO Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) in a way that ensures safety without unduly hindering necessary operational adjustments. The professional must exercise sound judgment to determine when a deviation from a SARP is a minor, acceptable variance and when it constitutes a significant safety risk requiring immediate and formal action. The correct approach involves a thorough assessment of the deviation against the intent and safety objectives of the relevant ICAO SARPs. This means understanding not just the letter of the regulation but also its underlying purpose. If the deviation, even if minor in operational terms, compromises the safety assurance provided by the SARP, then it must be addressed through formal channels, potentially involving reporting, investigation, and corrective action. This aligns with the overarching ICAO objective of achieving a globally harmonized level of aviation safety. The justification for this approach is rooted in the principle of safety first, which is paramount in aviation and is the foundational principle of ICAO SARPs. An incorrect approach would be to dismiss the deviation as insignificant without a proper safety assessment. This failure stems from a lack of due diligence and an underestimation of the cumulative impact of minor deviations. Ethically and regulatorily, this is unacceptable as it bypasses established safety management processes and could lead to a gradual erosion of safety standards. Another incorrect approach is to immediately escalate the issue without first attempting to understand the context and potential impact of the deviation. While caution is important, an overreaction without proper analysis can lead to unnecessary administrative burdens and can undermine trust in the reporting and safety management system. It fails to demonstrate professional judgment in assessing the severity of the issue. Professionals should employ a structured decision-making process when encountering deviations from ICAO SARPs. This process should include: 1) Identifying the specific ICAO SARP that appears to be affected. 2) Understanding the purpose and safety intent of that SARP. 3) Assessing the nature and extent of the deviation. 4) Evaluating the potential safety impact of the deviation, considering both immediate and cumulative effects. 5) Determining if the deviation compromises the safety assurance provided by the SARP. 6) If a safety compromise is identified, initiating the appropriate reporting and corrective action procedures as mandated by the relevant State’s aviation authority and ICAO guidance. If no safety compromise is identified, documenting the deviation and the rationale for its acceptance for future reference and continuous improvement.
-
Question 3 of 30
3. Question
Process analysis reveals that during a flight, a high-profile passenger expresses a strong desire for a significant deviation from the planned route to visit an unscheduled point of interest. The captain, while acknowledging the passenger’s request, feels uneasy about the potential impact on fuel reserves and air traffic control coordination. The first officer, observing the captain’s hesitation, appears hesitant to voice their own reservations. What is the most appropriate CRM-driven approach for the captain to manage this situation?
Correct
Scenario Analysis: This scenario is professionally challenging because it involves a critical decision point during a flight where a pilot’s judgment is directly influenced by external pressure and a potential deviation from standard operating procedures. The captain’s responsibility for the safe operation of the aircraft is paramount, and any compromise to this due to perceived pressure from a passenger, even a VIP, can have severe consequences. The need for clear communication and adherence to CRM principles is amplified in such situations to ensure all crew members feel empowered to voice concerns and that decisions are made based on safety, not external influence. Correct Approach Analysis: The correct approach involves the captain actively engaging the first officer in the decision-making process, seeking their input and ensuring they are comfortable with the proposed course of action. This aligns directly with the core tenets of Crew Resource Management (CRM), which emphasizes shared responsibility, open communication, and mutual support among the flight crew. Specifically, it upholds the principle of “advocacy and assertion,” where all crew members have the right and responsibility to voice concerns and challenge decisions if they believe safety is compromised. The captain’s role is to foster an environment where this can occur without fear of reprisal, ultimately leading to a safer outcome. This approach is supported by NBAA Professional Examinations’ emphasis on human factors and effective crew coordination. Incorrect Approaches Analysis: One incorrect approach involves the captain unilaterally making the decision to deviate from the planned route without adequately consulting or seeking the buy-in of the first officer. This fails to utilize the collective judgment of the crew, a fundamental CRM principle, and can lead to overlooked risks or a lack of shared situational awareness. It undermines the authority and responsibility of the first officer and can create a hierarchical dynamic that is detrimental to effective crew coordination. Another incorrect approach is for the captain to dismiss the first officer’s concerns outright and proceed with the passenger’s request without further discussion or consideration of the safety implications. This demonstrates a failure in leadership and CRM, as it discourages open communication and can create an environment where crew members are hesitant to speak up in the future. It prioritizes passenger satisfaction over flight safety, which is a direct contravention of aviation regulations and ethical responsibilities. A further incorrect approach would be for the captain to become defensive or dismissive of the first officer’s input, viewing it as insubordination rather than a safety concern. This creates a negative crew dynamic, erodes trust, and prevents the effective utilization of all available resources to ensure flight safety. It is a failure to recognize the value of diverse perspectives and the importance of a collaborative decision-making process. Professional Reasoning: Professionals should employ a structured decision-making process that prioritizes safety above all else. This involves: 1) Clearly identifying the situation and potential risks. 2) Actively seeking input from all relevant crew members, fostering an environment of open communication and mutual respect. 3) Evaluating all options based on established procedures, regulations, and safety considerations. 4) Making a clear, well-reasoned decision, ensuring all crew members understand the rationale. 5) Documenting the decision and rationale as appropriate. In situations involving passenger influence, the professional must remain objective and adhere to the highest safety standards, recognizing that the ultimate responsibility for the safe operation of the aircraft rests with the flight crew.
Incorrect
Scenario Analysis: This scenario is professionally challenging because it involves a critical decision point during a flight where a pilot’s judgment is directly influenced by external pressure and a potential deviation from standard operating procedures. The captain’s responsibility for the safe operation of the aircraft is paramount, and any compromise to this due to perceived pressure from a passenger, even a VIP, can have severe consequences. The need for clear communication and adherence to CRM principles is amplified in such situations to ensure all crew members feel empowered to voice concerns and that decisions are made based on safety, not external influence. Correct Approach Analysis: The correct approach involves the captain actively engaging the first officer in the decision-making process, seeking their input and ensuring they are comfortable with the proposed course of action. This aligns directly with the core tenets of Crew Resource Management (CRM), which emphasizes shared responsibility, open communication, and mutual support among the flight crew. Specifically, it upholds the principle of “advocacy and assertion,” where all crew members have the right and responsibility to voice concerns and challenge decisions if they believe safety is compromised. The captain’s role is to foster an environment where this can occur without fear of reprisal, ultimately leading to a safer outcome. This approach is supported by NBAA Professional Examinations’ emphasis on human factors and effective crew coordination. Incorrect Approaches Analysis: One incorrect approach involves the captain unilaterally making the decision to deviate from the planned route without adequately consulting or seeking the buy-in of the first officer. This fails to utilize the collective judgment of the crew, a fundamental CRM principle, and can lead to overlooked risks or a lack of shared situational awareness. It undermines the authority and responsibility of the first officer and can create a hierarchical dynamic that is detrimental to effective crew coordination. Another incorrect approach is for the captain to dismiss the first officer’s concerns outright and proceed with the passenger’s request without further discussion or consideration of the safety implications. This demonstrates a failure in leadership and CRM, as it discourages open communication and can create an environment where crew members are hesitant to speak up in the future. It prioritizes passenger satisfaction over flight safety, which is a direct contravention of aviation regulations and ethical responsibilities. A further incorrect approach would be for the captain to become defensive or dismissive of the first officer’s input, viewing it as insubordination rather than a safety concern. This creates a negative crew dynamic, erodes trust, and prevents the effective utilization of all available resources to ensure flight safety. It is a failure to recognize the value of diverse perspectives and the importance of a collaborative decision-making process. Professional Reasoning: Professionals should employ a structured decision-making process that prioritizes safety above all else. This involves: 1) Clearly identifying the situation and potential risks. 2) Actively seeking input from all relevant crew members, fostering an environment of open communication and mutual respect. 3) Evaluating all options based on established procedures, regulations, and safety considerations. 4) Making a clear, well-reasoned decision, ensuring all crew members understand the rationale. 5) Documenting the decision and rationale as appropriate. In situations involving passenger influence, the professional must remain objective and adhere to the highest safety standards, recognizing that the ultimate responsibility for the safe operation of the aircraft rests with the flight crew.
-
Question 4 of 30
4. Question
The audit findings indicate a potential deficiency in the company’s emergency response plan, specifically noting a lack of detailed procedures for communication with external agencies during a ground-based emergency involving a company aircraft. While no incident has occurred, the auditors have flagged this as a gap requiring attention. Considering the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework, which of the following actions is the most appropriate initial response?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires immediate and decisive action based on incomplete information, balancing the need for safety with operational continuity. The core of the challenge lies in interpreting audit findings that suggest a potential deficiency in emergency response planning without a clear indication of the severity or immediate threat. Professionals must exercise sound judgment, drawing upon their understanding of regulatory requirements and best practices to prioritize actions. The correct approach involves a systematic review and enhancement of the existing emergency response plan, focusing on identified gaps and ensuring compliance with NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework. This approach is right because it directly addresses the audit findings by proactively improving the organization’s preparedness. It aligns with the overarching regulatory expectation that aviation entities maintain robust and effective emergency response capabilities to mitigate risks to passengers, crew, and the public. Specifically, it demonstrates a commitment to due diligence and a proactive safety culture, which are implicitly and explicitly mandated by aviation safety regulations that emphasize risk management and continuous improvement. An incorrect approach that involves dismissing the audit findings due to a lack of immediate evidence of an incident is professionally unacceptable. This failure stems from a disregard for the proactive nature of safety regulations, which require organizations to anticipate and prepare for potential emergencies, not just react to them. It represents a significant ethical and regulatory failure, as it prioritizes operational convenience over the safety of all stakeholders. Another incorrect approach, such as immediately ceasing all operations without a clear and present danger, is also professionally unsound. While safety is paramount, such an extreme measure without a direct, imminent threat is an overreaction that can lead to unnecessary disruption and economic harm. It fails to demonstrate a balanced and risk-based approach to emergency preparedness, which is a cornerstone of responsible aviation management. A third incorrect approach, which involves only updating the plan based on a single, isolated incident without a broader review, is insufficient. This approach fails to address the systemic nature of emergency response planning. Audit findings often highlight underlying weaknesses that could manifest in various scenarios. A comprehensive review ensures that the plan is resilient and adaptable to a range of potential emergencies, not just those that have already occurred. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve: 1) Thoroughly understanding the audit findings and their potential implications. 2) Consulting relevant regulatory guidance and industry best practices. 3) Conducting a risk assessment to prioritize actions based on the likelihood and severity of potential emergencies. 4) Developing and implementing a phased plan for review and enhancement of the emergency response plan, involving relevant stakeholders. 5) Documenting all actions taken and decisions made.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires immediate and decisive action based on incomplete information, balancing the need for safety with operational continuity. The core of the challenge lies in interpreting audit findings that suggest a potential deficiency in emergency response planning without a clear indication of the severity or immediate threat. Professionals must exercise sound judgment, drawing upon their understanding of regulatory requirements and best practices to prioritize actions. The correct approach involves a systematic review and enhancement of the existing emergency response plan, focusing on identified gaps and ensuring compliance with NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework. This approach is right because it directly addresses the audit findings by proactively improving the organization’s preparedness. It aligns with the overarching regulatory expectation that aviation entities maintain robust and effective emergency response capabilities to mitigate risks to passengers, crew, and the public. Specifically, it demonstrates a commitment to due diligence and a proactive safety culture, which are implicitly and explicitly mandated by aviation safety regulations that emphasize risk management and continuous improvement. An incorrect approach that involves dismissing the audit findings due to a lack of immediate evidence of an incident is professionally unacceptable. This failure stems from a disregard for the proactive nature of safety regulations, which require organizations to anticipate and prepare for potential emergencies, not just react to them. It represents a significant ethical and regulatory failure, as it prioritizes operational convenience over the safety of all stakeholders. Another incorrect approach, such as immediately ceasing all operations without a clear and present danger, is also professionally unsound. While safety is paramount, such an extreme measure without a direct, imminent threat is an overreaction that can lead to unnecessary disruption and economic harm. It fails to demonstrate a balanced and risk-based approach to emergency preparedness, which is a cornerstone of responsible aviation management. A third incorrect approach, which involves only updating the plan based on a single, isolated incident without a broader review, is insufficient. This approach fails to address the systemic nature of emergency response planning. Audit findings often highlight underlying weaknesses that could manifest in various scenarios. A comprehensive review ensures that the plan is resilient and adaptable to a range of potential emergencies, not just those that have already occurred. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve: 1) Thoroughly understanding the audit findings and their potential implications. 2) Consulting relevant regulatory guidance and industry best practices. 3) Conducting a risk assessment to prioritize actions based on the likelihood and severity of potential emergencies. 4) Developing and implementing a phased plan for review and enhancement of the emergency response plan, involving relevant stakeholders. 5) Documenting all actions taken and decisions made.
-
Question 5 of 30
5. Question
Operational review demonstrates that an aircraft has undergone significant recent upgrades to its avionics and interior, and has a comprehensive maintenance history. When determining the aircraft’s fair market value for a regulatory filing under NBAA guidelines, which valuation approach best aligns with professional best practices and regulatory expectations?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because accurately valuing an aircraft, especially for regulatory purposes like those governed by the NBAA Professional Examinations framework, requires adherence to specific standards that go beyond mere market price. The challenge lies in selecting an approach that is not only financially sound but also compliant with the underlying principles of aviation regulation, which often prioritize safety, operational integrity, and fair market representation. Careful judgment is required to ensure the valuation method chosen is appropriate for the aircraft’s specific condition, operational history, and intended use, as dictated by NBAA guidelines. The correct approach involves utilizing a valuation methodology that is widely accepted within the aviation industry and aligns with the principles of the NBAA Professional Examinations. This typically means employing a combination of approaches, such as the cost approach, market approach, and income approach, where each is weighted appropriately based on the aircraft’s characteristics and the purpose of the valuation. The regulatory justification stems from the NBAA’s emphasis on professional standards that demand a thorough and objective assessment. Ethical considerations require transparency and a defensible methodology, ensuring that the valuation is not influenced by undue pressure or bias. An incorrect approach would be to solely rely on a single valuation method without considering its limitations or the specific context of the aircraft. For instance, using only the market approach might fail to account for unique modifications or the aircraft’s specific operational history, leading to an inaccurate representation of its true value. This would be a regulatory failure as it deviates from the comprehensive assessment expected under NBAA guidelines. Another incorrect approach is to base the valuation on subjective opinions or anecdotal evidence rather than established appraisal principles. This is an ethical failure as it compromises objectivity and professional integrity, potentially misleading stakeholders. Furthermore, neglecting to consider the aircraft’s maintenance records, airworthiness directives, and overall condition, which are critical factors in aviation valuation, would represent a significant professional oversight and a deviation from best practices mandated by aviation regulatory bodies. Professionals should approach aircraft valuation by first understanding the purpose of the valuation and the specific regulatory context (NBAA Professional Examinations). They should then identify all relevant data points, including maintenance history, operational hours, modifications, and market comparables. The next step is to select and apply appropriate valuation methodologies, considering the strengths and weaknesses of each in relation to the specific aircraft. Finally, the results should be synthesized into a well-supported conclusion, clearly articulating the methodology used and any assumptions made, ensuring compliance with NBAA standards for professional conduct and valuation accuracy.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because accurately valuing an aircraft, especially for regulatory purposes like those governed by the NBAA Professional Examinations framework, requires adherence to specific standards that go beyond mere market price. The challenge lies in selecting an approach that is not only financially sound but also compliant with the underlying principles of aviation regulation, which often prioritize safety, operational integrity, and fair market representation. Careful judgment is required to ensure the valuation method chosen is appropriate for the aircraft’s specific condition, operational history, and intended use, as dictated by NBAA guidelines. The correct approach involves utilizing a valuation methodology that is widely accepted within the aviation industry and aligns with the principles of the NBAA Professional Examinations. This typically means employing a combination of approaches, such as the cost approach, market approach, and income approach, where each is weighted appropriately based on the aircraft’s characteristics and the purpose of the valuation. The regulatory justification stems from the NBAA’s emphasis on professional standards that demand a thorough and objective assessment. Ethical considerations require transparency and a defensible methodology, ensuring that the valuation is not influenced by undue pressure or bias. An incorrect approach would be to solely rely on a single valuation method without considering its limitations or the specific context of the aircraft. For instance, using only the market approach might fail to account for unique modifications or the aircraft’s specific operational history, leading to an inaccurate representation of its true value. This would be a regulatory failure as it deviates from the comprehensive assessment expected under NBAA guidelines. Another incorrect approach is to base the valuation on subjective opinions or anecdotal evidence rather than established appraisal principles. This is an ethical failure as it compromises objectivity and professional integrity, potentially misleading stakeholders. Furthermore, neglecting to consider the aircraft’s maintenance records, airworthiness directives, and overall condition, which are critical factors in aviation valuation, would represent a significant professional oversight and a deviation from best practices mandated by aviation regulatory bodies. Professionals should approach aircraft valuation by first understanding the purpose of the valuation and the specific regulatory context (NBAA Professional Examinations). They should then identify all relevant data points, including maintenance history, operational hours, modifications, and market comparables. The next step is to select and apply appropriate valuation methodologies, considering the strengths and weaknesses of each in relation to the specific aircraft. Finally, the results should be synthesized into a well-supported conclusion, clearly articulating the methodology used and any assumptions made, ensuring compliance with NBAA standards for professional conduct and valuation accuracy.
-
Question 6 of 30
6. Question
Risk assessment procedures indicate that a fleet of business aircraft is approaching a significant maintenance interval. During the review of maintenance records, it is noted that several Airworthiness Directives (ADs) have compliance dates that fall within this upcoming interval, and a number of manufacturer Service Bulletins (SBs) have been released since the last major inspection. What is the most appropriate course of action for the Director of Maintenance to ensure regulatory compliance and operational safety?
Correct
This scenario presents a common implementation challenge in aviation maintenance: balancing operational demands with regulatory compliance regarding Airworthiness Directives (ADs) and Service Bulletins (SBs). The professional challenge lies in ensuring that mandatory safety requirements are met without unduly impacting aircraft availability, while also navigating the nuances between mandatory ADs and recommended SBs. Careful judgment is required to prioritize safety and compliance over expediency. The correct approach involves a systematic review of all applicable ADs and SBs for the specific aircraft type and serial number. This includes verifying that all ADs have been complied with within their specified compliance times and that any relevant SBs have been evaluated for applicability and potential implementation, especially those that may enhance safety or operational efficiency. The regulatory justification stems from the FAA’s (assuming US jurisdiction for NBAA Professional Examinations) mandate that all ADs must be complied with as a condition of continued airworthiness. Failure to comply with an AD renders an aircraft unairworthy. While SBs are not mandatory unless incorporated into an AD or type certificate, a prudent operator will evaluate them for safety enhancements. An incorrect approach would be to disregard an AD based on a perceived lack of immediate operational impact or to assume that an SB is automatically implemented without proper evaluation. Disregarding an AD, even if it appears minor, is a direct violation of FAA regulations and compromises the aircraft’s airworthiness. Assuming an SB is implemented without a proper review process fails to leverage potential safety improvements and could lead to inconsistent maintenance practices. Another incorrect approach would be to prioritize the implementation of SBs over overdue ADs, as ADs carry a higher regulatory imperative. This demonstrates a misunderstanding of the hierarchy of regulatory requirements and a failure to uphold the primary responsibility for ensuring continued airworthiness. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with identifying all applicable regulatory requirements (ADs). This is followed by a thorough assessment of their compliance status and due dates. Subsequently, relevant SBs should be reviewed for their potential benefits, with a decision made on their implementation based on a risk-benefit analysis and operational considerations, always ensuring that AD compliance remains paramount. This structured approach ensures that safety and regulatory compliance are the guiding principles in all maintenance decisions.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a common implementation challenge in aviation maintenance: balancing operational demands with regulatory compliance regarding Airworthiness Directives (ADs) and Service Bulletins (SBs). The professional challenge lies in ensuring that mandatory safety requirements are met without unduly impacting aircraft availability, while also navigating the nuances between mandatory ADs and recommended SBs. Careful judgment is required to prioritize safety and compliance over expediency. The correct approach involves a systematic review of all applicable ADs and SBs for the specific aircraft type and serial number. This includes verifying that all ADs have been complied with within their specified compliance times and that any relevant SBs have been evaluated for applicability and potential implementation, especially those that may enhance safety or operational efficiency. The regulatory justification stems from the FAA’s (assuming US jurisdiction for NBAA Professional Examinations) mandate that all ADs must be complied with as a condition of continued airworthiness. Failure to comply with an AD renders an aircraft unairworthy. While SBs are not mandatory unless incorporated into an AD or type certificate, a prudent operator will evaluate them for safety enhancements. An incorrect approach would be to disregard an AD based on a perceived lack of immediate operational impact or to assume that an SB is automatically implemented without proper evaluation. Disregarding an AD, even if it appears minor, is a direct violation of FAA regulations and compromises the aircraft’s airworthiness. Assuming an SB is implemented without a proper review process fails to leverage potential safety improvements and could lead to inconsistent maintenance practices. Another incorrect approach would be to prioritize the implementation of SBs over overdue ADs, as ADs carry a higher regulatory imperative. This demonstrates a misunderstanding of the hierarchy of regulatory requirements and a failure to uphold the primary responsibility for ensuring continued airworthiness. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with identifying all applicable regulatory requirements (ADs). This is followed by a thorough assessment of their compliance status and due dates. Subsequently, relevant SBs should be reviewed for their potential benefits, with a decision made on their implementation based on a risk-benefit analysis and operational considerations, always ensuring that AD compliance remains paramount. This structured approach ensures that safety and regulatory compliance are the guiding principles in all maintenance decisions.
-
Question 7 of 30
7. Question
The control framework reveals that an aviation company’s financial statements are being reviewed by multiple parties with distinct interests. A potential investor is seeking to understand the company’s long-term growth prospects and profitability, while a bank is assessing the company’s ability to service its debt obligations. A regulatory body is examining the company’s compliance with financial reporting standards and its overall financial stability. Which approach to analyzing the financial statements best serves the diverse needs of these stakeholders while upholding professional standards?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a financial analyst to interpret financial statements from the perspective of different stakeholders, each with unique interests and information needs, while adhering to the strict ethical and regulatory standards governing the NBAA Professional Examinations. The core challenge lies in prioritizing and presenting information in a way that is both accurate and relevant to the specific stakeholder’s decision-making process, without misrepresenting the financial health of the entity or violating professional conduct. The correct approach involves tailoring the financial statement analysis to the specific needs and objectives of each stakeholder group. For instance, an investor will focus on profitability, growth potential, and return on investment, while a creditor will prioritize liquidity, solvency, and the ability to repay debt. A regulator, on the other hand, will be concerned with compliance, financial stability, and adherence to industry standards. This approach is correct because it aligns with the fundamental ethical duty of professionals to act in the best interests of their clients or stakeholders, providing them with the most relevant and actionable insights derived from financial data. It also reflects the practical application of financial analysis, where the purpose of the analysis dictates the methodology and focus. The NBAA Professional Examinations implicitly expect candidates to demonstrate an understanding of how financial information serves diverse decision-making needs within the aviation industry. An incorrect approach would be to provide a generic, one-size-fits-all analysis that does not consider the distinct perspectives of each stakeholder. This fails to deliver value to any specific group and could lead to misinformed decisions. Ethically, it breaches the duty to provide relevant and tailored advice. Another incorrect approach would be to selectively highlight only positive aspects of the financial statements to please a particular stakeholder, ignoring potential risks or negative trends. This constitutes a misrepresentation of facts and a violation of the professional’s duty of integrity and objectivity, which are paramount under any professional examination framework, including those implicitly guiding NBAA professionals. Furthermore, focusing solely on historical performance without considering future implications or industry benchmarks would also be an incomplete and potentially misleading analysis, failing to meet the forward-looking needs of many stakeholders. The professional reasoning process for similar situations should involve first identifying all relevant stakeholders and understanding their primary objectives and concerns regarding the financial statements. Next, the analyst must determine which financial metrics and analytical techniques are most appropriate for each stakeholder’s needs. The analysis should then be conducted, ensuring accuracy and objectivity. Finally, the findings must be communicated clearly and concisely, tailored to the specific audience, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses, and providing context and implications for their decision-making. This structured approach ensures that the analysis is comprehensive, ethical, and maximally useful to those who rely on it.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a financial analyst to interpret financial statements from the perspective of different stakeholders, each with unique interests and information needs, while adhering to the strict ethical and regulatory standards governing the NBAA Professional Examinations. The core challenge lies in prioritizing and presenting information in a way that is both accurate and relevant to the specific stakeholder’s decision-making process, without misrepresenting the financial health of the entity or violating professional conduct. The correct approach involves tailoring the financial statement analysis to the specific needs and objectives of each stakeholder group. For instance, an investor will focus on profitability, growth potential, and return on investment, while a creditor will prioritize liquidity, solvency, and the ability to repay debt. A regulator, on the other hand, will be concerned with compliance, financial stability, and adherence to industry standards. This approach is correct because it aligns with the fundamental ethical duty of professionals to act in the best interests of their clients or stakeholders, providing them with the most relevant and actionable insights derived from financial data. It also reflects the practical application of financial analysis, where the purpose of the analysis dictates the methodology and focus. The NBAA Professional Examinations implicitly expect candidates to demonstrate an understanding of how financial information serves diverse decision-making needs within the aviation industry. An incorrect approach would be to provide a generic, one-size-fits-all analysis that does not consider the distinct perspectives of each stakeholder. This fails to deliver value to any specific group and could lead to misinformed decisions. Ethically, it breaches the duty to provide relevant and tailored advice. Another incorrect approach would be to selectively highlight only positive aspects of the financial statements to please a particular stakeholder, ignoring potential risks or negative trends. This constitutes a misrepresentation of facts and a violation of the professional’s duty of integrity and objectivity, which are paramount under any professional examination framework, including those implicitly guiding NBAA professionals. Furthermore, focusing solely on historical performance without considering future implications or industry benchmarks would also be an incomplete and potentially misleading analysis, failing to meet the forward-looking needs of many stakeholders. The professional reasoning process for similar situations should involve first identifying all relevant stakeholders and understanding their primary objectives and concerns regarding the financial statements. Next, the analyst must determine which financial metrics and analytical techniques are most appropriate for each stakeholder’s needs. The analysis should then be conducted, ensuring accuracy and objectivity. Finally, the findings must be communicated clearly and concisely, tailored to the specific audience, highlighting both strengths and weaknesses, and providing context and implications for their decision-making. This structured approach ensures that the analysis is comprehensive, ethical, and maximally useful to those who rely on it.
-
Question 8 of 30
8. Question
Operational review demonstrates that a US-based charter operator is planning a series of flights for a foreign-registered aircraft that will be temporarily operating within the United States for a period of six months, carrying both cargo and passengers. The operator has not previously handled foreign-registered aircraft for extended periods and is unsure of the precise Customs and Border Protection (CBP) declaration and entry requirements beyond standard international flight plans. Which of the following approaches best ensures regulatory compliance with CBP regulations for this operation?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge due to the critical nature of Customs and Border Protection (CBP) regulations in aviation operations. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines, aircraft seizure, and operational disruptions, impacting both the company’s financial health and its reputation. The need for meticulous adherence to these regulations is paramount, requiring a thorough understanding of import/export requirements, aircraft documentation, and passenger/crew manifest accuracy. The correct approach involves proactively engaging with CBP to clarify the specific requirements for the aircraft’s intended use, including any temporary import or export provisions that may apply. This proactive engagement ensures that all necessary documentation is prepared accurately and submitted in a timely manner, demonstrating a commitment to regulatory compliance. This aligns with the overarching principle of due diligence and the legal obligation to comply with all applicable CBP laws and regulations. By seeking clarification, the operator avoids assumptions and ensures that their actions are fully aligned with CBP expectations, thereby mitigating risk. An incorrect approach would be to assume that standard international flight procedures are sufficient without verifying specific CBP requirements for the aircraft’s unique operational context. This assumption risks overlooking critical documentation or declaration requirements, leading to potential violations. Another incorrect approach would be to delay engagement with CBP until the last minute, hoping to resolve any issues upon arrival. This reactive stance significantly increases the likelihood of encountering unforeseen complications, delays, and penalties, as CBP may not have adequate time to process requests or grant necessary permissions. Finally, attempting to bypass or misrepresent information to CBP, even with the intention of expediting the process, constitutes a serious regulatory and ethical breach, undermining the integrity of the aviation system and exposing the operator to severe legal repercussions. Professionals facing similar situations should adopt a systematic decision-making process. This involves: 1) Identifying the specific regulatory framework applicable to the operation (in this case, US CBP regulations). 2) Thoroughly researching and understanding the relevant regulations pertaining to the intended flight, including any specific provisions for aircraft importation, exportation, or transit. 3) Proactively seeking clarification from the relevant regulatory authority (CBP) regarding any ambiguities or specific requirements. 4) Developing a comprehensive compliance plan that addresses all identified regulatory obligations. 5) Implementing the plan diligently and maintaining accurate records. 6) Regularly reviewing and updating the compliance plan to reflect any changes in regulations or operational procedures.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge due to the critical nature of Customs and Border Protection (CBP) regulations in aviation operations. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, including fines, aircraft seizure, and operational disruptions, impacting both the company’s financial health and its reputation. The need for meticulous adherence to these regulations is paramount, requiring a thorough understanding of import/export requirements, aircraft documentation, and passenger/crew manifest accuracy. The correct approach involves proactively engaging with CBP to clarify the specific requirements for the aircraft’s intended use, including any temporary import or export provisions that may apply. This proactive engagement ensures that all necessary documentation is prepared accurately and submitted in a timely manner, demonstrating a commitment to regulatory compliance. This aligns with the overarching principle of due diligence and the legal obligation to comply with all applicable CBP laws and regulations. By seeking clarification, the operator avoids assumptions and ensures that their actions are fully aligned with CBP expectations, thereby mitigating risk. An incorrect approach would be to assume that standard international flight procedures are sufficient without verifying specific CBP requirements for the aircraft’s unique operational context. This assumption risks overlooking critical documentation or declaration requirements, leading to potential violations. Another incorrect approach would be to delay engagement with CBP until the last minute, hoping to resolve any issues upon arrival. This reactive stance significantly increases the likelihood of encountering unforeseen complications, delays, and penalties, as CBP may not have adequate time to process requests or grant necessary permissions. Finally, attempting to bypass or misrepresent information to CBP, even with the intention of expediting the process, constitutes a serious regulatory and ethical breach, undermining the integrity of the aviation system and exposing the operator to severe legal repercussions. Professionals facing similar situations should adopt a systematic decision-making process. This involves: 1) Identifying the specific regulatory framework applicable to the operation (in this case, US CBP regulations). 2) Thoroughly researching and understanding the relevant regulations pertaining to the intended flight, including any specific provisions for aircraft importation, exportation, or transit. 3) Proactively seeking clarification from the relevant regulatory authority (CBP) regarding any ambiguities or specific requirements. 4) Developing a comprehensive compliance plan that addresses all identified regulatory obligations. 5) Implementing the plan diligently and maintaining accurate records. 6) Regularly reviewing and updating the compliance plan to reflect any changes in regulations or operational procedures.
-
Question 9 of 30
9. Question
The evaluation methodology shows that a mechanic has verbally confirmed that all required maintenance tasks for an aircraft’s annual inspection have been completed and signed off in the aircraft’s maintenance logbook. However, due to an impending flight schedule, the inspector is under significant time pressure to release the aircraft for service. The inspector has not personally reviewed each individual entry in the logbook for completeness and accuracy, but trusts the mechanic’s assurance. What is the most professionally responsible course of action for the inspector?
Correct
This scenario presents a professionally challenging situation due to the critical nature of accurate and complete maintenance record keeping in aviation. The challenge lies in balancing the immediate operational pressure to return an aircraft to service with the non-negotiable regulatory requirement for thorough documentation. Failure to adhere to these requirements can have severe consequences, including regulatory penalties, operational disruptions, and most importantly, compromised aviation safety. Careful judgment is required to ensure that all necessary steps are taken, even under time constraints. The correct approach involves meticulously reviewing all maintenance logs, ensuring that every action taken is properly documented, signed off by authorized personnel, and cross-referenced with the relevant maintenance manual procedures. This approach is right because it directly aligns with the absolute priority placed on maintenance record keeping by aviation regulatory frameworks, such as those enforced by the FAA in the United States. Specifically, regulations like 14 CFR Part 43, which governs general operating and flight rules, and Part 91, which outlines general flight rules, mandate that all maintenance, preventive maintenance, alterations, and inspections be recorded. These records serve as the official history of the aircraft’s airworthiness and are essential for demonstrating compliance with airworthiness directives and manufacturer service bulletins. Adhering to this approach ensures that the aircraft’s maintenance history is transparent, verifiable, and compliant, upholding the highest standards of aviation safety and regulatory adherence. An incorrect approach of relying solely on verbal confirmation from the mechanic, without verifying the physical logbook entries, represents a significant regulatory and ethical failure. This bypasses the fundamental requirement for written documentation, which is the legally recognized proof of maintenance performed. It also fails to account for potential errors, omissions, or misinterpretations that can occur in verbal communication, especially under pressure. Such an approach directly contravenes the spirit and letter of regulations requiring detailed and accurate record-keeping. Another incorrect approach, which is to assume the records are complete because the aircraft is being returned to service, is also a critical failure. This demonstrates a lack of diligence and an abdication of responsibility. The assumption of completeness is not a substitute for verification. Regulatory bodies expect proactive verification of records, not passive acceptance. This approach risks overlooking critical discrepancies that could impact airworthiness and safety. Finally, an incorrect approach of prioritizing the return of the aircraft to service over the complete and accurate recording of maintenance actions, even if the mechanic states they will “catch up on the paperwork later,” is a severe regulatory and ethical lapse. This prioritizes operational expediency over safety and compliance. Aviation regulations are designed to ensure safety through rigorous documentation, and any deviation from this principle is unacceptable. The “catch-up” approach is inherently risky, as it increases the likelihood of errors, omissions, or the loss of critical information, thereby compromising the integrity of the aircraft’s maintenance history and potentially its airworthiness. The professional reasoning process for similar situations should involve a systematic approach: first, understand the regulatory requirements for record keeping in the specific jurisdiction. Second, assess the operational context and any time pressures, but never allow these to override safety and compliance mandates. Third, implement a verification process that includes reviewing physical records, cross-referencing with technical data, and confirming authorized sign-offs. Fourth, if any discrepancies are found, address them immediately and ensure they are corrected and properly documented before the aircraft is released for operation. Finally, maintain a commitment to continuous improvement in record-keeping practices.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professionally challenging situation due to the critical nature of accurate and complete maintenance record keeping in aviation. The challenge lies in balancing the immediate operational pressure to return an aircraft to service with the non-negotiable regulatory requirement for thorough documentation. Failure to adhere to these requirements can have severe consequences, including regulatory penalties, operational disruptions, and most importantly, compromised aviation safety. Careful judgment is required to ensure that all necessary steps are taken, even under time constraints. The correct approach involves meticulously reviewing all maintenance logs, ensuring that every action taken is properly documented, signed off by authorized personnel, and cross-referenced with the relevant maintenance manual procedures. This approach is right because it directly aligns with the absolute priority placed on maintenance record keeping by aviation regulatory frameworks, such as those enforced by the FAA in the United States. Specifically, regulations like 14 CFR Part 43, which governs general operating and flight rules, and Part 91, which outlines general flight rules, mandate that all maintenance, preventive maintenance, alterations, and inspections be recorded. These records serve as the official history of the aircraft’s airworthiness and are essential for demonstrating compliance with airworthiness directives and manufacturer service bulletins. Adhering to this approach ensures that the aircraft’s maintenance history is transparent, verifiable, and compliant, upholding the highest standards of aviation safety and regulatory adherence. An incorrect approach of relying solely on verbal confirmation from the mechanic, without verifying the physical logbook entries, represents a significant regulatory and ethical failure. This bypasses the fundamental requirement for written documentation, which is the legally recognized proof of maintenance performed. It also fails to account for potential errors, omissions, or misinterpretations that can occur in verbal communication, especially under pressure. Such an approach directly contravenes the spirit and letter of regulations requiring detailed and accurate record-keeping. Another incorrect approach, which is to assume the records are complete because the aircraft is being returned to service, is also a critical failure. This demonstrates a lack of diligence and an abdication of responsibility. The assumption of completeness is not a substitute for verification. Regulatory bodies expect proactive verification of records, not passive acceptance. This approach risks overlooking critical discrepancies that could impact airworthiness and safety. Finally, an incorrect approach of prioritizing the return of the aircraft to service over the complete and accurate recording of maintenance actions, even if the mechanic states they will “catch up on the paperwork later,” is a severe regulatory and ethical lapse. This prioritizes operational expediency over safety and compliance. Aviation regulations are designed to ensure safety through rigorous documentation, and any deviation from this principle is unacceptable. The “catch-up” approach is inherently risky, as it increases the likelihood of errors, omissions, or the loss of critical information, thereby compromising the integrity of the aircraft’s maintenance history and potentially its airworthiness. The professional reasoning process for similar situations should involve a systematic approach: first, understand the regulatory requirements for record keeping in the specific jurisdiction. Second, assess the operational context and any time pressures, but never allow these to override safety and compliance mandates. Third, implement a verification process that includes reviewing physical records, cross-referencing with technical data, and confirming authorized sign-offs. Fourth, if any discrepancies are found, address them immediately and ensure they are corrected and properly documented before the aircraft is released for operation. Finally, maintain a commitment to continuous improvement in record-keeping practices.
-
Question 10 of 30
10. Question
Process analysis reveals that a key internal control designed to prevent unauthorized expenditures in a flight department has a documented weakness. The compliance officer estimates that, if exploited, this weakness could lead to an average of \$5,000 in unauthorized expenditures per instance. The flight department operates 10 aircraft, and historical data indicates that such control weaknesses have, on average, been exploited once every two years. The compliance officer is deciding on the scope and frequency of the next audit cycle for this control. What is the most appropriate approach for determining the audit scope and frequency?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires the compliance officer to balance the need for thorough auditing with the practical constraints of time and resources, while strictly adhering to the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework. The core of the challenge lies in accurately quantifying the financial impact of a potential compliance breach and then determining the appropriate level of audit intensity based on that risk. The correct approach involves a data-driven risk assessment to prioritize audit efforts. This means calculating the potential financial exposure associated with the identified control weakness. If the estimated financial exposure is significant, a more comprehensive and frequent audit is warranted. This aligns with the principles of effective compliance programs, which mandate a risk-based approach to resource allocation and audit planning. The NBAA Professional Examinations’ framework implicitly supports this by emphasizing the importance of identifying and mitigating risks that could lead to financial penalties or reputational damage. An incorrect approach would be to conduct a superficial review without quantifying the potential financial impact. This fails to establish a clear risk profile and may lead to under-auditing areas of high potential exposure or over-auditing areas of low risk, thus misallocating valuable resources and potentially leaving the organization vulnerable. Another incorrect approach is to rely solely on the frequency of past issues without considering the magnitude of potential financial loss. While historical data is useful, it does not fully capture the current risk landscape, especially if the nature or scale of operations has changed. A third incorrect approach is to assume that a minor control weakness automatically translates to a minor financial risk without any attempt at quantification. This overlooks the potential for compounding effects or unforeseen consequences that could escalate a seemingly small issue into a significant financial problem. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with identifying potential compliance risks. For each identified risk, they must then attempt to quantify the potential financial impact. This quantification should consider factors such as the likelihood of the control failure occurring and the severity of the consequences if it does. Based on this risk assessment, audit resources should be allocated proportionally, with higher-risk areas receiving more attention. This systematic, data-driven approach ensures that compliance efforts are focused where they are most needed and are most effective in protecting the organization.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires the compliance officer to balance the need for thorough auditing with the practical constraints of time and resources, while strictly adhering to the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework. The core of the challenge lies in accurately quantifying the financial impact of a potential compliance breach and then determining the appropriate level of audit intensity based on that risk. The correct approach involves a data-driven risk assessment to prioritize audit efforts. This means calculating the potential financial exposure associated with the identified control weakness. If the estimated financial exposure is significant, a more comprehensive and frequent audit is warranted. This aligns with the principles of effective compliance programs, which mandate a risk-based approach to resource allocation and audit planning. The NBAA Professional Examinations’ framework implicitly supports this by emphasizing the importance of identifying and mitigating risks that could lead to financial penalties or reputational damage. An incorrect approach would be to conduct a superficial review without quantifying the potential financial impact. This fails to establish a clear risk profile and may lead to under-auditing areas of high potential exposure or over-auditing areas of low risk, thus misallocating valuable resources and potentially leaving the organization vulnerable. Another incorrect approach is to rely solely on the frequency of past issues without considering the magnitude of potential financial loss. While historical data is useful, it does not fully capture the current risk landscape, especially if the nature or scale of operations has changed. A third incorrect approach is to assume that a minor control weakness automatically translates to a minor financial risk without any attempt at quantification. This overlooks the potential for compounding effects or unforeseen consequences that could escalate a seemingly small issue into a significant financial problem. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with identifying potential compliance risks. For each identified risk, they must then attempt to quantify the potential financial impact. This quantification should consider factors such as the likelihood of the control failure occurring and the severity of the consequences if it does. Based on this risk assessment, audit resources should be allocated proportionally, with higher-risk areas receiving more attention. This systematic, data-driven approach ensures that compliance efforts are focused where they are most needed and are most effective in protecting the organization.
-
Question 11 of 30
11. Question
The risk matrix shows a low probability, low impact anomaly during a pre-flight baggage screening process where a non-standard item was detected in a passenger’s checked luggage. The item, a common household tool, was flagged by the screening technology but did not trigger a high-level alert. The ground crew is eager to maintain the flight schedule. Which of the following actions best adheres to TSA and DHS security regulations?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires an aviation professional to balance operational efficiency with stringent security mandates from the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). The pressure to maintain flight schedules and passenger flow can create a temptation to overlook or minimize security protocols, especially when faced with perceived minor deviations. However, the absolute priority of security regulations necessitates a rigorous and unwavering adherence, even when it might cause operational inconvenience. The correct approach involves a thorough and documented investigation of the anomaly, prioritizing the security directive over immediate operational expediency. This aligns directly with TSA and DHS mandates that emphasize a zero-tolerance policy for security breaches and require proactive identification and mitigation of potential threats. The regulatory framework demands that any deviation from established security procedures, regardless of perceived severity, must be addressed through established protocols, which typically include reporting, investigation, and potential corrective actions. This ensures the integrity of the security system and upholds the overarching goal of aviation safety and security. An incorrect approach that involves dismissing the anomaly due to its perceived minor nature is a direct violation of TSA and DHS security directives. This demonstrates a failure to understand the layered nature of aviation security, where seemingly small issues can be indicators of larger vulnerabilities or intentional circumvention of rules. Ethically, it represents a dereliction of duty to protect passengers and crew. Another incorrect approach, which is to immediately implement a workaround without proper authorization or investigation, bypasses critical security checks and could inadvertently create new security risks or mask an ongoing threat. This approach prioritizes speed over security, which is fundamentally contrary to the principles of aviation security regulations. It also fails to document the incident and the resolution, hindering future security assessments and training. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with a clear understanding of the applicable security regulations (TSA and DHS). When an anomaly is detected, the immediate step is to halt operations or isolate the situation as dictated by the specific security protocol. This is followed by a systematic and documented investigation, involving relevant security personnel. The decision on how to proceed should be based on the findings of the investigation and in strict accordance with established security procedures and regulatory guidance. If there is any doubt, escalating the issue to the appropriate security authority is paramount. The ultimate goal is to ensure that security is never compromised for the sake of operational convenience.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires an aviation professional to balance operational efficiency with stringent security mandates from the Transportation Security Administration (TSA) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). The pressure to maintain flight schedules and passenger flow can create a temptation to overlook or minimize security protocols, especially when faced with perceived minor deviations. However, the absolute priority of security regulations necessitates a rigorous and unwavering adherence, even when it might cause operational inconvenience. The correct approach involves a thorough and documented investigation of the anomaly, prioritizing the security directive over immediate operational expediency. This aligns directly with TSA and DHS mandates that emphasize a zero-tolerance policy for security breaches and require proactive identification and mitigation of potential threats. The regulatory framework demands that any deviation from established security procedures, regardless of perceived severity, must be addressed through established protocols, which typically include reporting, investigation, and potential corrective actions. This ensures the integrity of the security system and upholds the overarching goal of aviation safety and security. An incorrect approach that involves dismissing the anomaly due to its perceived minor nature is a direct violation of TSA and DHS security directives. This demonstrates a failure to understand the layered nature of aviation security, where seemingly small issues can be indicators of larger vulnerabilities or intentional circumvention of rules. Ethically, it represents a dereliction of duty to protect passengers and crew. Another incorrect approach, which is to immediately implement a workaround without proper authorization or investigation, bypasses critical security checks and could inadvertently create new security risks or mask an ongoing threat. This approach prioritizes speed over security, which is fundamentally contrary to the principles of aviation security regulations. It also fails to document the incident and the resolution, hindering future security assessments and training. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with a clear understanding of the applicable security regulations (TSA and DHS). When an anomaly is detected, the immediate step is to halt operations or isolate the situation as dictated by the specific security protocol. This is followed by a systematic and documented investigation, involving relevant security personnel. The decision on how to proceed should be based on the findings of the investigation and in strict accordance with established security procedures and regulatory guidance. If there is any doubt, escalating the issue to the appropriate security authority is paramount. The ultimate goal is to ensure that security is never compromised for the sake of operational convenience.
-
Question 12 of 30
12. Question
The monitoring system demonstrates a recurring pattern of minor system failures that, while not immediately catastrophic, have led to intermittent operational disruptions. The insured’s business interruption insurance policy contains a clause that excludes coverage for “loss resulting from any gradual deterioration, inherent vice, or latent defect.” The insurer has denied the claim for lost profits resulting from these disruptions, citing this exclusion. The insured believes the policy should cover these losses, arguing that the failures are a result of specific component malfunctions rather than gradual deterioration. Which of the following approaches represents the most appropriate professional response to this situation? a) Advise the insured to accept the insurer’s denial based on the exclusion, as the insurer is the expert in interpreting policy language. b) Conduct a thorough review of the policy’s “Definitions” section, the specific wording of the exclusion clause, and any relevant endorsements or riders to determine if the “minor system failures” fall within the scope of “gradual deterioration” or if they constitute distinct malfunctions covered by the policy. c) Recommend that the insured immediately file a lawsuit against the insurer, as the insurer’s denial is likely an attempt to avoid payment. d) Rely on general industry knowledge about how similar exclusions are typically applied to business interruption claims to advise the insured.
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires interpreting an insurance policy’s wording in the context of an actual event, where ambiguity can lead to significant financial and operational consequences for the insured. The core difficulty lies in determining whether the policy’s exclusions or conditions apply to the situation, necessitating a thorough understanding of insurance contract law and the specific policy’s language. Careful judgment is required to avoid misinterpreting the policy, which could result in denied claims or inadequate coverage. The correct approach involves a meticulous review of the policy’s “Definitions” section, the specific clause in question, and any relevant endorsements or riders. This approach is best professional practice because it adheres to the principle of interpreting insurance contracts according to their plain meaning, while also considering the intent of the parties and any established legal precedents for similar policy language. Regulatory frameworks, such as those governing insurance contracts, typically mandate that policy terms be interpreted in a manner that is fair and reasonable to the insured, and that ambiguities are construed against the insurer. This methodical examination ensures that the interpretation is grounded in the contract’s explicit terms and applicable legal standards, thereby upholding the duty of care owed to the client. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on the insurer’s initial assessment without independent policy review fails to uphold the insured’s rights. This is a regulatory failure because it bypasses the contractual obligations and the insured’s right to a fair claim assessment based on the policy’s terms. It also represents an ethical failure to act in the client’s best interest. Another incorrect approach that relies on industry custom or common practice without direct reference to the policy wording is also problematic. While industry norms can provide context, they cannot override explicit policy language. This approach risks misinterpreting the specific agreement between the parties and could lead to a violation of contractual obligations, as insurance policies are legally binding contracts that must be interpreted on their own terms. A further incorrect approach that prioritizes expediency over thoroughness, such as making a decision based on a quick glance at the exclusion clause, is a significant professional failing. This demonstrates a lack of due diligence and a disregard for the potential impact on the insured. It violates the professional standard of care and could lead to a breach of fiduciary duty if applicable, as well as potential regulatory sanctions for inadequate claim handling. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve: 1) A comprehensive review of all relevant policy documents, including endorsements and exclusions. 2) A clear understanding of the factual circumstances of the claim. 3) Research into any applicable legal precedents or regulatory guidance related to the specific policy language. 4) Consultation with legal counsel or insurance experts if ambiguity persists. 5) A reasoned determination based on the policy’s plain meaning, intent, and legal context, always prioritizing the client’s interests within the bounds of the contract and regulations.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires interpreting an insurance policy’s wording in the context of an actual event, where ambiguity can lead to significant financial and operational consequences for the insured. The core difficulty lies in determining whether the policy’s exclusions or conditions apply to the situation, necessitating a thorough understanding of insurance contract law and the specific policy’s language. Careful judgment is required to avoid misinterpreting the policy, which could result in denied claims or inadequate coverage. The correct approach involves a meticulous review of the policy’s “Definitions” section, the specific clause in question, and any relevant endorsements or riders. This approach is best professional practice because it adheres to the principle of interpreting insurance contracts according to their plain meaning, while also considering the intent of the parties and any established legal precedents for similar policy language. Regulatory frameworks, such as those governing insurance contracts, typically mandate that policy terms be interpreted in a manner that is fair and reasonable to the insured, and that ambiguities are construed against the insurer. This methodical examination ensures that the interpretation is grounded in the contract’s explicit terms and applicable legal standards, thereby upholding the duty of care owed to the client. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on the insurer’s initial assessment without independent policy review fails to uphold the insured’s rights. This is a regulatory failure because it bypasses the contractual obligations and the insured’s right to a fair claim assessment based on the policy’s terms. It also represents an ethical failure to act in the client’s best interest. Another incorrect approach that relies on industry custom or common practice without direct reference to the policy wording is also problematic. While industry norms can provide context, they cannot override explicit policy language. This approach risks misinterpreting the specific agreement between the parties and could lead to a violation of contractual obligations, as insurance policies are legally binding contracts that must be interpreted on their own terms. A further incorrect approach that prioritizes expediency over thoroughness, such as making a decision based on a quick glance at the exclusion clause, is a significant professional failing. This demonstrates a lack of due diligence and a disregard for the potential impact on the insured. It violates the professional standard of care and could lead to a breach of fiduciary duty if applicable, as well as potential regulatory sanctions for inadequate claim handling. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve: 1) A comprehensive review of all relevant policy documents, including endorsements and exclusions. 2) A clear understanding of the factual circumstances of the claim. 3) Research into any applicable legal precedents or regulatory guidance related to the specific policy language. 4) Consultation with legal counsel or insurance experts if ambiguity persists. 5) A reasoned determination based on the policy’s plain meaning, intent, and legal context, always prioritizing the client’s interests within the bounds of the contract and regulations.
-
Question 13 of 30
13. Question
The assessment process reveals a pilot observing an unusual vibration during taxiing that is not immediately identifiable as a critical system failure but is outside normal operational parameters. The pilot is concerned about a potential safety issue but is also aware of an impending departure time critical for passenger connections. What is the most appropriate course of action for the pilot to ensure aviation safety and security in this situation?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires an aviation professional to balance operational efficiency with the paramount importance of aviation safety and security, specifically in the context of regulatory compliance. The pressure to maintain schedules and meet operational demands can create a temptation to overlook or downplay potential safety or security concerns. Careful judgment is required to ensure that all identified risks are addressed appropriately according to established protocols and regulations, without succumbing to external pressures. The correct approach involves a systematic and documented process of risk assessment and mitigation, directly aligned with the principles of aviation safety management systems (SMS) as mandated by regulatory frameworks such as those governing the NBAA Professional Examinations. This approach prioritizes the identification, evaluation, and control of hazards. Specifically, it requires the immediate reporting of the observed anomaly to the appropriate safety personnel, followed by a thorough investigation to determine the root cause and implement corrective actions. This aligns with the proactive safety culture encouraged by aviation authorities, where all personnel are empowered and obligated to report safety concerns without fear of reprisal. The regulatory justification lies in the overarching requirement for operators to maintain a safe and secure environment, which is achieved through robust SMS and adherence to reporting and investigation procedures. An incorrect approach that involves dismissing the anomaly due to its perceived minor nature fails to acknowledge the ‘no-blame’ reporting culture and the potential for seemingly small issues to escalate into significant safety events. This approach neglects the fundamental principle of aviation safety that all anomalies, regardless of perceived severity, warrant investigation. Ethically, it demonstrates a lack of commitment to the safety of passengers, crew, and the public. Another incorrect approach, which is to address the anomaly informally without documentation or formal reporting, bypasses the established safety management system. This failure to document and formally investigate prevents the organization from learning from the incident, identifying systemic weaknesses, and implementing effective long-term solutions. It also undermines the integrity of the safety reporting system and can lead to a perception that safety concerns are not taken seriously, thereby eroding the safety culture. A further incorrect approach, which is to delay reporting until a more convenient time, directly contradicts the urgency required in addressing potential safety or security issues. Aviation safety regulations emphasize timely reporting and response to ensure that risks are managed before they can manifest as incidents or accidents. This delay can expose the aircraft, crew, and passengers to unnecessary risks and may also violate specific reporting timelines stipulated by regulatory bodies. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a clear understanding of the organization’s Safety Management System (SMS) and its reporting procedures. Professionals should be trained to recognize potential hazards, understand the importance of immediate and accurate reporting, and be empowered to escalate concerns without fear of retribution. When faced with an anomaly, the decision-making framework should prioritize: 1) immediate assessment of the situation for any imminent danger, 2) adherence to established reporting protocols, 3) participation in the investigation process, and 4) implementation of corrective actions as directed. This systematic approach ensures that safety and security remain the highest priorities, in accordance with regulatory mandates and ethical responsibilities.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires an aviation professional to balance operational efficiency with the paramount importance of aviation safety and security, specifically in the context of regulatory compliance. The pressure to maintain schedules and meet operational demands can create a temptation to overlook or downplay potential safety or security concerns. Careful judgment is required to ensure that all identified risks are addressed appropriately according to established protocols and regulations, without succumbing to external pressures. The correct approach involves a systematic and documented process of risk assessment and mitigation, directly aligned with the principles of aviation safety management systems (SMS) as mandated by regulatory frameworks such as those governing the NBAA Professional Examinations. This approach prioritizes the identification, evaluation, and control of hazards. Specifically, it requires the immediate reporting of the observed anomaly to the appropriate safety personnel, followed by a thorough investigation to determine the root cause and implement corrective actions. This aligns with the proactive safety culture encouraged by aviation authorities, where all personnel are empowered and obligated to report safety concerns without fear of reprisal. The regulatory justification lies in the overarching requirement for operators to maintain a safe and secure environment, which is achieved through robust SMS and adherence to reporting and investigation procedures. An incorrect approach that involves dismissing the anomaly due to its perceived minor nature fails to acknowledge the ‘no-blame’ reporting culture and the potential for seemingly small issues to escalate into significant safety events. This approach neglects the fundamental principle of aviation safety that all anomalies, regardless of perceived severity, warrant investigation. Ethically, it demonstrates a lack of commitment to the safety of passengers, crew, and the public. Another incorrect approach, which is to address the anomaly informally without documentation or formal reporting, bypasses the established safety management system. This failure to document and formally investigate prevents the organization from learning from the incident, identifying systemic weaknesses, and implementing effective long-term solutions. It also undermines the integrity of the safety reporting system and can lead to a perception that safety concerns are not taken seriously, thereby eroding the safety culture. A further incorrect approach, which is to delay reporting until a more convenient time, directly contradicts the urgency required in addressing potential safety or security issues. Aviation safety regulations emphasize timely reporting and response to ensure that risks are managed before they can manifest as incidents or accidents. This delay can expose the aircraft, crew, and passengers to unnecessary risks and may also violate specific reporting timelines stipulated by regulatory bodies. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a clear understanding of the organization’s Safety Management System (SMS) and its reporting procedures. Professionals should be trained to recognize potential hazards, understand the importance of immediate and accurate reporting, and be empowered to escalate concerns without fear of retribution. When faced with an anomaly, the decision-making framework should prioritize: 1) immediate assessment of the situation for any imminent danger, 2) adherence to established reporting protocols, 3) participation in the investigation process, and 4) implementation of corrective actions as directed. This systematic approach ensures that safety and security remain the highest priorities, in accordance with regulatory mandates and ethical responsibilities.
-
Question 14 of 30
14. Question
Governance review demonstrates that when acquiring a new aircraft, the most prudent method for ensuring the transaction’s integrity and compliance with applicable regulations and best practices involves a multi-disciplinary approach. Which of the following best describes this approach?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because aircraft purchase agreements are complex legal documents with significant financial implications. Ensuring compliance with the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework, which implicitly governs business aviation operations and transactions within the United States, requires a thorough understanding of applicable federal aviation regulations, contract law principles, and ethical business practices. The challenge lies in identifying the most appropriate method for reviewing and approving such agreements to mitigate risks and ensure the transaction aligns with the buyer’s operational needs and financial capacity, all while adhering to industry best practices and regulatory expectations. The correct approach involves a comprehensive legal and operational review by qualified professionals. This entails engaging legal counsel specializing in aviation transactions to scrutinize the agreement for compliance with all relevant federal laws and regulations (e.g., FAA regulations pertaining to aircraft registration, airworthiness, and operational standards), identifying potential liabilities, and ensuring favorable terms. Simultaneously, operational and technical experts should assess the aircraft’s condition, maintenance history, and suitability for the intended mission, verifying that the agreement accurately reflects the asset being purchased and its operational capabilities. This multi-faceted review ensures that all aspects of the transaction are sound, legally defensible, and operationally viable, aligning with the highest standards of due diligence expected in business aviation. An incorrect approach would be to rely solely on the seller’s representations without independent verification. This fails to meet the professional obligation to conduct thorough due diligence, potentially exposing the buyer to undisclosed defects, non-compliance issues, or unfavorable contractual terms. Such an approach risks violating principles of good faith and fair dealing inherent in contract law and could lead to significant financial losses or operational disruptions. Another incorrect approach is to delegate the entire review process to a single individual without the necessary specialized expertise. For instance, a finance manager might focus solely on the financial aspects, neglecting critical legal or technical considerations. This siloed approach overlooks crucial elements that could render the purchase problematic or non-compliant, demonstrating a failure to apply a holistic and expert-driven review process. A further incorrect approach is to prioritize speed over thoroughness, rushing the review process to close the deal quickly. While efficiency is valued, it should not come at the expense of due diligence. Expedited reviews that bypass essential legal, technical, or operational checks can lead to overlooking critical issues, resulting in a flawed transaction that could have long-term negative consequences. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve establishing a clear checklist for aircraft purchase agreement reviews, identifying key stakeholders (legal counsel, technical advisors, operational managers, financial analysts), and allocating sufficient time and resources for each stage of the review. A risk-based approach should be employed, prioritizing the identification and mitigation of the most significant potential issues. Transparency and clear communication among all parties involved are paramount to ensure a well-informed and compliant transaction.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because aircraft purchase agreements are complex legal documents with significant financial implications. Ensuring compliance with the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework, which implicitly governs business aviation operations and transactions within the United States, requires a thorough understanding of applicable federal aviation regulations, contract law principles, and ethical business practices. The challenge lies in identifying the most appropriate method for reviewing and approving such agreements to mitigate risks and ensure the transaction aligns with the buyer’s operational needs and financial capacity, all while adhering to industry best practices and regulatory expectations. The correct approach involves a comprehensive legal and operational review by qualified professionals. This entails engaging legal counsel specializing in aviation transactions to scrutinize the agreement for compliance with all relevant federal laws and regulations (e.g., FAA regulations pertaining to aircraft registration, airworthiness, and operational standards), identifying potential liabilities, and ensuring favorable terms. Simultaneously, operational and technical experts should assess the aircraft’s condition, maintenance history, and suitability for the intended mission, verifying that the agreement accurately reflects the asset being purchased and its operational capabilities. This multi-faceted review ensures that all aspects of the transaction are sound, legally defensible, and operationally viable, aligning with the highest standards of due diligence expected in business aviation. An incorrect approach would be to rely solely on the seller’s representations without independent verification. This fails to meet the professional obligation to conduct thorough due diligence, potentially exposing the buyer to undisclosed defects, non-compliance issues, or unfavorable contractual terms. Such an approach risks violating principles of good faith and fair dealing inherent in contract law and could lead to significant financial losses or operational disruptions. Another incorrect approach is to delegate the entire review process to a single individual without the necessary specialized expertise. For instance, a finance manager might focus solely on the financial aspects, neglecting critical legal or technical considerations. This siloed approach overlooks crucial elements that could render the purchase problematic or non-compliant, demonstrating a failure to apply a holistic and expert-driven review process. A further incorrect approach is to prioritize speed over thoroughness, rushing the review process to close the deal quickly. While efficiency is valued, it should not come at the expense of due diligence. Expedited reviews that bypass essential legal, technical, or operational checks can lead to overlooking critical issues, resulting in a flawed transaction that could have long-term negative consequences. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve establishing a clear checklist for aircraft purchase agreement reviews, identifying key stakeholders (legal counsel, technical advisors, operational managers, financial analysts), and allocating sufficient time and resources for each stage of the review. A risk-based approach should be employed, prioritizing the identification and mitigation of the most significant potential issues. Transparency and clear communication among all parties involved are paramount to ensure a well-informed and compliant transaction.
-
Question 15 of 30
15. Question
Market research demonstrates that a growing number of aviation organizations are seeking leadership that can effectively navigate complex regulatory environments while fostering a culture of innovation and safety. Considering the paramount importance of compliance and operational excellence in aviation, which leadership approach is most likely to achieve these dual objectives and align with the professional standards expected in the NBAA Professional Examinations?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires balancing the immediate needs and expectations of various stakeholders with the long-term strategic direction of the organization, all while adhering to the ethical and regulatory standards governing the NBAA Professional Examinations. The challenge lies in discerning which leadership style is most effective in fostering a culture of continuous improvement and compliance within the context of aviation operations, where safety and regulatory adherence are paramount. Careful judgment is required to avoid leadership approaches that could inadvertently compromise safety, lead to regulatory non-compliance, or alienate key personnel. The correct approach involves a transformational leadership style, characterized by inspiring and motivating individuals to achieve organizational goals beyond their immediate self-interest. This style encourages innovation, ethical behavior, and a shared commitment to excellence, which are critical for maintaining high standards in aviation. Specifically, a transformational leader would articulate a clear vision for safety and compliance, empower team members to identify and address potential risks, and foster an environment where open communication about concerns is encouraged. This aligns with the NBAA’s emphasis on professionalism, safety, and adherence to best practices, which are implicitly supported by regulatory frameworks that prioritize a proactive safety culture. An autocratic leadership style, which centralizes decision-making and relies on command and control, is incorrect because it can stifle initiative, discourage reporting of safety concerns, and create an environment of fear rather than collaboration. This approach is antithetical to the principles of a robust safety management system, which requires input and vigilance from all levels of the organization. Such a style could lead to overlooking critical safety issues or creating a perception of non-compliance due to a lack of open dialogue. A laissez-faire leadership style, characterized by a hands-off approach and minimal intervention, is also incorrect. While it may foster autonomy, it can lead to a lack of direction, accountability, and consistent adherence to standards. In an aviation context, this could result in inconsistent safety protocols, a decline in regulatory compliance, and an inability to effectively manage operational risks. This style fails to provide the necessary oversight and guidance to ensure that all stakeholders are aligned with the organization’s safety and compliance objectives. A transactional leadership style, which focuses on rewards and punishments to achieve compliance, is less effective than transformational leadership in fostering a deeply ingrained safety culture. While it can ensure adherence to specific rules, it may not inspire the proactive engagement and commitment necessary for continuous improvement and the anticipation of emerging risks. It can create a compliance-driven environment rather than a safety-driven one, where individuals may only act to avoid penalties rather than out of a genuine commitment to safety. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a thorough assessment of the organizational culture, the specific operational context, and the diverse needs of stakeholders. Professionals should consider how different leadership styles might impact safety, compliance, and employee morale. They should prioritize leadership approaches that promote open communication, empower individuals, foster accountability, and align with the overarching ethical and regulatory requirements of the aviation industry, as implicitly guided by the standards expected in NBAA Professional Examinations.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires balancing the immediate needs and expectations of various stakeholders with the long-term strategic direction of the organization, all while adhering to the ethical and regulatory standards governing the NBAA Professional Examinations. The challenge lies in discerning which leadership style is most effective in fostering a culture of continuous improvement and compliance within the context of aviation operations, where safety and regulatory adherence are paramount. Careful judgment is required to avoid leadership approaches that could inadvertently compromise safety, lead to regulatory non-compliance, or alienate key personnel. The correct approach involves a transformational leadership style, characterized by inspiring and motivating individuals to achieve organizational goals beyond their immediate self-interest. This style encourages innovation, ethical behavior, and a shared commitment to excellence, which are critical for maintaining high standards in aviation. Specifically, a transformational leader would articulate a clear vision for safety and compliance, empower team members to identify and address potential risks, and foster an environment where open communication about concerns is encouraged. This aligns with the NBAA’s emphasis on professionalism, safety, and adherence to best practices, which are implicitly supported by regulatory frameworks that prioritize a proactive safety culture. An autocratic leadership style, which centralizes decision-making and relies on command and control, is incorrect because it can stifle initiative, discourage reporting of safety concerns, and create an environment of fear rather than collaboration. This approach is antithetical to the principles of a robust safety management system, which requires input and vigilance from all levels of the organization. Such a style could lead to overlooking critical safety issues or creating a perception of non-compliance due to a lack of open dialogue. A laissez-faire leadership style, characterized by a hands-off approach and minimal intervention, is also incorrect. While it may foster autonomy, it can lead to a lack of direction, accountability, and consistent adherence to standards. In an aviation context, this could result in inconsistent safety protocols, a decline in regulatory compliance, and an inability to effectively manage operational risks. This style fails to provide the necessary oversight and guidance to ensure that all stakeholders are aligned with the organization’s safety and compliance objectives. A transactional leadership style, which focuses on rewards and punishments to achieve compliance, is less effective than transformational leadership in fostering a deeply ingrained safety culture. While it can ensure adherence to specific rules, it may not inspire the proactive engagement and commitment necessary for continuous improvement and the anticipation of emerging risks. It can create a compliance-driven environment rather than a safety-driven one, where individuals may only act to avoid penalties rather than out of a genuine commitment to safety. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a thorough assessment of the organizational culture, the specific operational context, and the diverse needs of stakeholders. Professionals should consider how different leadership styles might impact safety, compliance, and employee morale. They should prioritize leadership approaches that promote open communication, empower individuals, foster accountability, and align with the overarching ethical and regulatory requirements of the aviation industry, as implicitly guided by the standards expected in NBAA Professional Examinations.
-
Question 16 of 30
16. Question
What factors determine the most appropriate leasing and financing option for an aircraft acquisition under US regulatory and financial frameworks, considering the operator’s long-term strategic objectives and financial capacity?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because selecting the appropriate leasing and financing option for an aircraft requires a nuanced understanding of both financial principles and the specific regulatory landscape governing aviation transactions within the United States. Professionals must navigate complex financial instruments while ensuring strict adherence to FAA regulations, tax laws, and any applicable state-specific requirements. The decision impacts the operator’s financial health, operational flexibility, and compliance status. The correct approach involves a comprehensive evaluation of the operator’s current and projected financial position, operational needs, and long-term strategic goals, balanced against the specific terms, costs, and residual value implications of each financing or leasing option. This includes a thorough due diligence process to understand the legal, tax, and operational consequences of each structure. Regulatory justification stems from the FAA’s oversight of aircraft operations and ownership, which implicitly requires that financing structures do not circumvent safety regulations or create undue financial burdens that could compromise operational integrity. Furthermore, tax implications must align with IRS guidelines, and any lease agreements must comply with contract law. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on minimizing upfront costs without considering long-term residual value or maintenance obligations would be professionally unsound. This failure stems from a lack of comprehensive financial planning and potentially overlooks regulatory requirements related to aircraft condition and maintenance, which are often tied to lease terms. Another incorrect approach that prioritizes a specific type of financing (e.g., outright purchase) without objectively assessing its suitability against other options like operating leases or finance leases would be a failure of due diligence. This demonstrates a bias that could lead to a suboptimal financial outcome and potentially non-compliance if the chosen structure creates unforeseen regulatory hurdles. A third incorrect approach that neglects to consult with legal and tax professionals regarding the intricacies of the chosen structure would be a significant ethical and professional lapse, as it risks non-compliance with federal and state laws governing aircraft acquisition and operation. Professionals should employ a structured decision-making process that begins with clearly defining the operational and financial objectives. This should be followed by thorough research into available leasing and financing options, including a detailed analysis of their respective terms, costs, benefits, and risks. Crucially, this research must be informed by consultation with legal counsel specializing in aviation law and tax advisors to ensure full regulatory compliance and optimal financial structuring. A comparative analysis of the viable options, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors, should then guide the final selection.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because selecting the appropriate leasing and financing option for an aircraft requires a nuanced understanding of both financial principles and the specific regulatory landscape governing aviation transactions within the United States. Professionals must navigate complex financial instruments while ensuring strict adherence to FAA regulations, tax laws, and any applicable state-specific requirements. The decision impacts the operator’s financial health, operational flexibility, and compliance status. The correct approach involves a comprehensive evaluation of the operator’s current and projected financial position, operational needs, and long-term strategic goals, balanced against the specific terms, costs, and residual value implications of each financing or leasing option. This includes a thorough due diligence process to understand the legal, tax, and operational consequences of each structure. Regulatory justification stems from the FAA’s oversight of aircraft operations and ownership, which implicitly requires that financing structures do not circumvent safety regulations or create undue financial burdens that could compromise operational integrity. Furthermore, tax implications must align with IRS guidelines, and any lease agreements must comply with contract law. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on minimizing upfront costs without considering long-term residual value or maintenance obligations would be professionally unsound. This failure stems from a lack of comprehensive financial planning and potentially overlooks regulatory requirements related to aircraft condition and maintenance, which are often tied to lease terms. Another incorrect approach that prioritizes a specific type of financing (e.g., outright purchase) without objectively assessing its suitability against other options like operating leases or finance leases would be a failure of due diligence. This demonstrates a bias that could lead to a suboptimal financial outcome and potentially non-compliance if the chosen structure creates unforeseen regulatory hurdles. A third incorrect approach that neglects to consult with legal and tax professionals regarding the intricacies of the chosen structure would be a significant ethical and professional lapse, as it risks non-compliance with federal and state laws governing aircraft acquisition and operation. Professionals should employ a structured decision-making process that begins with clearly defining the operational and financial objectives. This should be followed by thorough research into available leasing and financing options, including a detailed analysis of their respective terms, costs, benefits, and risks. Crucially, this research must be informed by consultation with legal counsel specializing in aviation law and tax advisors to ensure full regulatory compliance and optimal financial structuring. A comparative analysis of the viable options, considering both quantitative and qualitative factors, should then guide the final selection.
-
Question 17 of 30
17. Question
Strategic planning requires a proactive approach to managing aircraft operations. A Part 91 operator is considering implementing a new flight planning software that promises significant cost savings through optimized routing and fuel management. However, the software’s algorithms have not been explicitly vetted against the aircraft’s specific performance data or the latest FAA advisory circulars concerning fuel planning. What is the most appropriate course of action for the Director of Operations?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge in aircraft operations and management by requiring a decision that balances operational efficiency with regulatory compliance and safety. The challenge lies in interpreting and applying the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework, which emphasizes adherence to established guidelines for aircraft operations. Careful judgment is required to ensure that any proposed operational change does not inadvertently violate safety standards or operational limitations. The correct approach involves a thorough review of the aircraft’s operational manual, relevant FAA regulations (as implied by the NBAA context), and the specific limitations of the aircraft’s avionics and performance envelopes. This approach is correct because it prioritizes safety and compliance, which are paramount in aviation. It ensures that any operational decision is grounded in documented procedures and regulatory requirements, thereby mitigating risks and maintaining the highest standards of airworthiness and operational integrity. This aligns with the core principles of responsible aircraft management and the overarching goal of preventing accidents and incidents. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on cost savings without a comprehensive safety and regulatory review would be professionally unacceptable. This failure stems from a disregard for established safety protocols and regulatory mandates, potentially leading to unsafe operating conditions or violations. Another incorrect approach that relies on anecdotal evidence or informal advice from other operators, bypassing official documentation and regulatory guidance, is also professionally flawed. This method introduces significant risk by not adhering to the verified and approved operational parameters, potentially leading to operational errors or non-compliance. A third incorrect approach that prioritizes schedule adherence above all else, even if it means pushing the aircraft or crew beyond established limits, is ethically and regulatorally unsound. This demonstrates a failure to uphold the primary responsibility of ensuring the safety of flight operations, which must always take precedence over scheduling demands. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with identifying the operational objective. This is followed by a comprehensive assessment of all relevant regulatory requirements, aircraft limitations, and operational manuals. Potential solutions are then evaluated against these parameters, with a strong emphasis on safety and compliance. The chosen solution must be justifiable based on documented evidence and regulatory adherence, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and that the decision is transparent and defensible.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge in aircraft operations and management by requiring a decision that balances operational efficiency with regulatory compliance and safety. The challenge lies in interpreting and applying the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework, which emphasizes adherence to established guidelines for aircraft operations. Careful judgment is required to ensure that any proposed operational change does not inadvertently violate safety standards or operational limitations. The correct approach involves a thorough review of the aircraft’s operational manual, relevant FAA regulations (as implied by the NBAA context), and the specific limitations of the aircraft’s avionics and performance envelopes. This approach is correct because it prioritizes safety and compliance, which are paramount in aviation. It ensures that any operational decision is grounded in documented procedures and regulatory requirements, thereby mitigating risks and maintaining the highest standards of airworthiness and operational integrity. This aligns with the core principles of responsible aircraft management and the overarching goal of preventing accidents and incidents. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on cost savings without a comprehensive safety and regulatory review would be professionally unacceptable. This failure stems from a disregard for established safety protocols and regulatory mandates, potentially leading to unsafe operating conditions or violations. Another incorrect approach that relies on anecdotal evidence or informal advice from other operators, bypassing official documentation and regulatory guidance, is also professionally flawed. This method introduces significant risk by not adhering to the verified and approved operational parameters, potentially leading to operational errors or non-compliance. A third incorrect approach that prioritizes schedule adherence above all else, even if it means pushing the aircraft or crew beyond established limits, is ethically and regulatorally unsound. This demonstrates a failure to uphold the primary responsibility of ensuring the safety of flight operations, which must always take precedence over scheduling demands. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with identifying the operational objective. This is followed by a comprehensive assessment of all relevant regulatory requirements, aircraft limitations, and operational manuals. Potential solutions are then evaluated against these parameters, with a strong emphasis on safety and compliance. The chosen solution must be justifiable based on documented evidence and regulatory adherence, ensuring that all stakeholders are informed and that the decision is transparent and defensible.
-
Question 18 of 30
18. Question
Benchmark analysis indicates that an aviation organization is experiencing an increase in sophisticated cyber-attacks targeting its flight planning systems. Which of the following represents the most compliant and effective approach to addressing this escalating security threat, in accordance with NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a nuanced understanding of the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework concerning security threat assessments, balancing proactive risk mitigation with operational efficiency and compliance. The core challenge lies in identifying and implementing appropriate security measures without unduly burdening operations or violating specific NBAA guidelines. Careful judgment is required to ensure that the assessment is comprehensive, proportionate, and aligned with the organization’s specific operational context and the regulatory expectations. The correct approach involves a systematic and documented process for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential security threats relevant to the organization’s operations, as mandated by NBAA Professional Examinations’ guidelines. This approach emphasizes a proactive stance, integrating security considerations into operational planning and decision-making. It requires a thorough understanding of the specific types of threats that could impact aviation operations, such as insider threats, cyber threats, physical security breaches, and acts of unlawful interference. The regulatory justification stems from the NBAA’s emphasis on maintaining a secure operating environment, which is a fundamental responsibility for all aviation professionals. This systematic approach ensures that risks are managed effectively and that the organization remains compliant with all applicable security regulations and best practices. An incorrect approach that relies solely on reactive measures, addressing security threats only after an incident has occurred, fails to meet the proactive requirements of the NBAA framework. This reactive stance is inherently less effective and can lead to significant operational disruptions, reputational damage, and potential regulatory penalties. It demonstrates a lack of foresight and a failure to implement preventative controls, which are central to robust security management. Another incorrect approach that focuses on implementing generic, one-size-fits-all security measures without a specific threat assessment is also professionally unacceptable. This approach is inefficient, potentially costly, and may not adequately address the unique vulnerabilities of the organization. It lacks the targeted analysis required by the NBAA guidelines, which expect security measures to be tailored to identified risks. A third incorrect approach that prioritizes cost savings over comprehensive security assessment, leading to the omission of critical threat mitigation strategies, is a direct violation of the NBAA’s commitment to safety and security. Financial considerations should not supersede the imperative to protect assets, personnel, and the integrity of operations. This approach demonstrates a disregard for the potential consequences of inadequate security and a failure to uphold professional responsibilities. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a structured risk management framework. This begins with identifying potential threats relevant to the specific operational environment. Following identification, a thorough analysis of the likelihood and impact of each threat is crucial. Based on this analysis, appropriate mitigation strategies should be developed and implemented, with a clear plan for ongoing monitoring and review. This process ensures that security measures are proportionate, effective, and aligned with regulatory requirements and organizational objectives.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a nuanced understanding of the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework concerning security threat assessments, balancing proactive risk mitigation with operational efficiency and compliance. The core challenge lies in identifying and implementing appropriate security measures without unduly burdening operations or violating specific NBAA guidelines. Careful judgment is required to ensure that the assessment is comprehensive, proportionate, and aligned with the organization’s specific operational context and the regulatory expectations. The correct approach involves a systematic and documented process for identifying, analyzing, and mitigating potential security threats relevant to the organization’s operations, as mandated by NBAA Professional Examinations’ guidelines. This approach emphasizes a proactive stance, integrating security considerations into operational planning and decision-making. It requires a thorough understanding of the specific types of threats that could impact aviation operations, such as insider threats, cyber threats, physical security breaches, and acts of unlawful interference. The regulatory justification stems from the NBAA’s emphasis on maintaining a secure operating environment, which is a fundamental responsibility for all aviation professionals. This systematic approach ensures that risks are managed effectively and that the organization remains compliant with all applicable security regulations and best practices. An incorrect approach that relies solely on reactive measures, addressing security threats only after an incident has occurred, fails to meet the proactive requirements of the NBAA framework. This reactive stance is inherently less effective and can lead to significant operational disruptions, reputational damage, and potential regulatory penalties. It demonstrates a lack of foresight and a failure to implement preventative controls, which are central to robust security management. Another incorrect approach that focuses on implementing generic, one-size-fits-all security measures without a specific threat assessment is also professionally unacceptable. This approach is inefficient, potentially costly, and may not adequately address the unique vulnerabilities of the organization. It lacks the targeted analysis required by the NBAA guidelines, which expect security measures to be tailored to identified risks. A third incorrect approach that prioritizes cost savings over comprehensive security assessment, leading to the omission of critical threat mitigation strategies, is a direct violation of the NBAA’s commitment to safety and security. Financial considerations should not supersede the imperative to protect assets, personnel, and the integrity of operations. This approach demonstrates a disregard for the potential consequences of inadequate security and a failure to uphold professional responsibilities. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a structured risk management framework. This begins with identifying potential threats relevant to the specific operational environment. Following identification, a thorough analysis of the likelihood and impact of each threat is crucial. Based on this analysis, appropriate mitigation strategies should be developed and implemented, with a clear plan for ongoing monitoring and review. This process ensures that security measures are proportionate, effective, and aligned with regulatory requirements and organizational objectives.
-
Question 19 of 30
19. Question
During the evaluation of an aircraft’s readiness for departure in a reported light freezing drizzle environment, the flight crew observes no visible ice or frost on the wings. However, the outside air temperature is -2°C, and the forecast indicates the freezing drizzle is expected to continue for the next hour. The flight is scheduled to depart within 15 minutes. What is the most appropriate course of action to ensure flight safety?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires the flight crew to make a critical decision regarding de-icing and anti-icing procedures under time pressure and potentially adverse weather conditions, directly impacting flight safety. The decision involves balancing operational efficiency with the absolute requirement to prevent ice accumulation on critical aircraft surfaces. The professional challenge lies in accurately assessing the environmental conditions, understanding the limitations and capabilities of available de-icing/anti-icing fluids and equipment, and adhering strictly to the aircraft manufacturer’s and regulatory guidelines. The correct approach involves a thorough pre-flight assessment of weather forecasts and current conditions, a clear understanding of the aircraft’s specific de-icing and anti-icing requirements as outlined in the Aircraft Flight Manual (AFM) and relevant operational procedures, and the execution of the chosen procedure based on these factors. This approach is correct because it prioritizes safety by ensuring that the aircraft’s critical surfaces are free of contamination before takeoff, thereby preventing loss of lift and control. Adherence to the AFM and regulatory guidance (e.g., FAA AC 91-74B, AC 120-16E, or equivalent if specified by the exam jurisdiction) is paramount. This includes understanding holdover times, fluid types, and application methods, all of which are designed to mitigate the risks associated with in-flight icing. An incorrect approach that relies solely on visual inspection without considering the potential for subtle contamination or without verifying holdover times is professionally unacceptable. This fails to meet the regulatory requirement for ensuring a clean aircraft, as visual inspection alone can be misleading, especially in conditions where frost or thin ice may not be readily apparent. It also disregards the scientific basis of holdover times, which are crucial for determining the effectiveness of anti-icing fluids. Another incorrect approach that involves proceeding with takeoff despite a known or suspected contamination on critical surfaces, perhaps due to schedule pressure, is a severe regulatory and ethical failure. This directly violates the fundamental principle of flight safety and the explicit prohibitions against taking off with contaminated surfaces. It demonstrates a disregard for the manufacturer’s limitations and regulatory mandates designed to prevent catastrophic failures. A further incorrect approach that involves using unapproved de-icing fluids or equipment not specified by the manufacturer or regulatory authorities is also professionally unacceptable. This introduces unknown variables into the de-icing/anti-icing process, potentially compromising the effectiveness of the treatment and leading to unforeseen hazards. It bypasses established safety protocols and testing, creating a significant risk. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory framework and the aircraft’s specific operational requirements. This involves proactive weather monitoring, consultation of AFM and operational manuals, and clear communication within the flight crew and with ground personnel. When faced with ambiguous conditions or time constraints, the default decision should always be to err on the side of caution, prioritizing the removal of all doubt regarding aircraft contamination over operational expediency. This systematic approach ensures that all safety-critical aspects are addressed before flight.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires the flight crew to make a critical decision regarding de-icing and anti-icing procedures under time pressure and potentially adverse weather conditions, directly impacting flight safety. The decision involves balancing operational efficiency with the absolute requirement to prevent ice accumulation on critical aircraft surfaces. The professional challenge lies in accurately assessing the environmental conditions, understanding the limitations and capabilities of available de-icing/anti-icing fluids and equipment, and adhering strictly to the aircraft manufacturer’s and regulatory guidelines. The correct approach involves a thorough pre-flight assessment of weather forecasts and current conditions, a clear understanding of the aircraft’s specific de-icing and anti-icing requirements as outlined in the Aircraft Flight Manual (AFM) and relevant operational procedures, and the execution of the chosen procedure based on these factors. This approach is correct because it prioritizes safety by ensuring that the aircraft’s critical surfaces are free of contamination before takeoff, thereby preventing loss of lift and control. Adherence to the AFM and regulatory guidance (e.g., FAA AC 91-74B, AC 120-16E, or equivalent if specified by the exam jurisdiction) is paramount. This includes understanding holdover times, fluid types, and application methods, all of which are designed to mitigate the risks associated with in-flight icing. An incorrect approach that relies solely on visual inspection without considering the potential for subtle contamination or without verifying holdover times is professionally unacceptable. This fails to meet the regulatory requirement for ensuring a clean aircraft, as visual inspection alone can be misleading, especially in conditions where frost or thin ice may not be readily apparent. It also disregards the scientific basis of holdover times, which are crucial for determining the effectiveness of anti-icing fluids. Another incorrect approach that involves proceeding with takeoff despite a known or suspected contamination on critical surfaces, perhaps due to schedule pressure, is a severe regulatory and ethical failure. This directly violates the fundamental principle of flight safety and the explicit prohibitions against taking off with contaminated surfaces. It demonstrates a disregard for the manufacturer’s limitations and regulatory mandates designed to prevent catastrophic failures. A further incorrect approach that involves using unapproved de-icing fluids or equipment not specified by the manufacturer or regulatory authorities is also professionally unacceptable. This introduces unknown variables into the de-icing/anti-icing process, potentially compromising the effectiveness of the treatment and leading to unforeseen hazards. It bypasses established safety protocols and testing, creating a significant risk. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory framework and the aircraft’s specific operational requirements. This involves proactive weather monitoring, consultation of AFM and operational manuals, and clear communication within the flight crew and with ground personnel. When faced with ambiguous conditions or time constraints, the default decision should always be to err on the side of caution, prioritizing the removal of all doubt regarding aircraft contamination over operational expediency. This systematic approach ensures that all safety-critical aspects are addressed before flight.
-
Question 20 of 30
20. Question
Cost-benefit analysis shows that an operator of a turboprop aircraft valued at $3,000,000, used for executive charter operations, faces a potential total hull loss with a probability of 0.005 annually. The annual premium for full hull coverage with a $50,000 deductible is $45,000. The operator is considering a policy with a $250,000 deductible, costing $25,000 annually, believing the lower premium offers better value. What is the expected annual cost of hull loss for each deductible option, and which option represents the more prudent financial decision based on minimizing expected financial exposure?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires a nuanced understanding of aviation insurance coverage types and their application to specific operational risks, moving beyond a superficial understanding to a quantitative assessment. The challenge lies in accurately calculating the potential financial impact of a specific risk and then determining the most cost-effective insurance solution that aligns with regulatory requirements and prudent business practice. Careful judgment is required to balance the cost of premiums against the potential financial exposure and the availability of coverage under different policy types. The correct approach involves a thorough analysis of the aircraft’s operational profile, potential liabilities, and the specific risks associated with its use. This includes understanding the limits and exclusions of various aviation insurance policies, such as hull insurance, liability insurance (including passenger liability, third-party liability, and cargo liability), and potentially specialized coverages like war risk or aerial application liability. The correct approach would involve calculating the potential financial loss from a specific incident (e.g., a hull loss or a significant third-party claim) and comparing this to the cost of obtaining adequate coverage. For instance, if the aircraft’s hull value is $5,000,000 and the annual premium for full hull coverage is $50,000, while the potential financial exposure from a total loss is $5,000,000, the cost-benefit analysis favors purchasing the hull insurance. This aligns with the NBAA Professional Examinations’ emphasis on responsible operational management and financial stewardship, which implicitly requires adequate risk mitigation through appropriate insurance. Regulatory frameworks, while not dictating specific insurance types for all operations, mandate financial responsibility for operators, making prudent insurance choices a de facto requirement for compliance and operational continuity. An incorrect approach would be to solely focus on the lowest premium without considering the scope of coverage. For example, opting for a policy with a very high deductible or significant exclusions to reduce the annual premium might leave the operator exposed to substantial financial losses in the event of an incident. This would be a regulatory failure as it could compromise the operator’s ability to meet financial responsibility requirements. Another incorrect approach would be to assume that a standard liability policy adequately covers all potential risks, neglecting specialized coverages that might be necessary for the specific type of operation (e.g., charter operations, aerial spraying). This oversight could lead to significant uncovered claims, violating the principle of prudent risk management and potentially contravening any specific regulatory mandates for financial responsibility related to the operation. A third incorrect approach would be to underinsure the hull value of the aircraft, believing that a partial loss is the only significant risk. This would fail to account for the possibility of a total loss, leaving the operator with a substantial financial deficit if the aircraft is destroyed. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a systematic risk assessment, followed by a detailed evaluation of available insurance products. This includes understanding policy wordings, exclusions, and limitations. Professionals should consult with experienced aviation insurance brokers who understand the specific regulatory environment and operational risks. The decision should be based on a quantitative analysis of potential losses versus the cost of coverage, ensuring that the chosen insurance program provides adequate protection against significant financial events, thereby ensuring operational viability and compliance with financial responsibility regulations.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires a nuanced understanding of aviation insurance coverage types and their application to specific operational risks, moving beyond a superficial understanding to a quantitative assessment. The challenge lies in accurately calculating the potential financial impact of a specific risk and then determining the most cost-effective insurance solution that aligns with regulatory requirements and prudent business practice. Careful judgment is required to balance the cost of premiums against the potential financial exposure and the availability of coverage under different policy types. The correct approach involves a thorough analysis of the aircraft’s operational profile, potential liabilities, and the specific risks associated with its use. This includes understanding the limits and exclusions of various aviation insurance policies, such as hull insurance, liability insurance (including passenger liability, third-party liability, and cargo liability), and potentially specialized coverages like war risk or aerial application liability. The correct approach would involve calculating the potential financial loss from a specific incident (e.g., a hull loss or a significant third-party claim) and comparing this to the cost of obtaining adequate coverage. For instance, if the aircraft’s hull value is $5,000,000 and the annual premium for full hull coverage is $50,000, while the potential financial exposure from a total loss is $5,000,000, the cost-benefit analysis favors purchasing the hull insurance. This aligns with the NBAA Professional Examinations’ emphasis on responsible operational management and financial stewardship, which implicitly requires adequate risk mitigation through appropriate insurance. Regulatory frameworks, while not dictating specific insurance types for all operations, mandate financial responsibility for operators, making prudent insurance choices a de facto requirement for compliance and operational continuity. An incorrect approach would be to solely focus on the lowest premium without considering the scope of coverage. For example, opting for a policy with a very high deductible or significant exclusions to reduce the annual premium might leave the operator exposed to substantial financial losses in the event of an incident. This would be a regulatory failure as it could compromise the operator’s ability to meet financial responsibility requirements. Another incorrect approach would be to assume that a standard liability policy adequately covers all potential risks, neglecting specialized coverages that might be necessary for the specific type of operation (e.g., charter operations, aerial spraying). This oversight could lead to significant uncovered claims, violating the principle of prudent risk management and potentially contravening any specific regulatory mandates for financial responsibility related to the operation. A third incorrect approach would be to underinsure the hull value of the aircraft, believing that a partial loss is the only significant risk. This would fail to account for the possibility of a total loss, leaving the operator with a substantial financial deficit if the aircraft is destroyed. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a systematic risk assessment, followed by a detailed evaluation of available insurance products. This includes understanding policy wordings, exclusions, and limitations. Professionals should consult with experienced aviation insurance brokers who understand the specific regulatory environment and operational risks. The decision should be based on a quantitative analysis of potential losses versus the cost of coverage, ensuring that the chosen insurance program provides adequate protection against significant financial events, thereby ensuring operational viability and compliance with financial responsibility regulations.
-
Question 21 of 30
21. Question
The control framework reveals that during a flight, a passenger suddenly collapses and appears to be unresponsive and not breathing. The cabin crew member has completed basic first aid training. What is the most appropriate immediate course of action?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires immediate decision-making under pressure, balancing the immediate need for medical assistance with the potential for further harm or legal ramifications. The professional’s duty of care extends to ensuring the well-being of individuals in their care, which includes responding appropriately to medical emergencies. The core of the challenge lies in understanding the scope of one’s responsibilities and the appropriate actions to take within the established regulatory framework, without overstepping professional boundaries or failing to provide necessary aid. The correct approach involves recognizing the severity of the situation, initiating immediate emergency medical services, and providing basic first aid within the limits of one’s training and competence. This aligns with the NBAA Professional Examinations’ emphasis on safety and responsible conduct. Regulatory frameworks, such as those governing aviation professionals, typically mandate a duty of care to assist in emergencies, provided it does not place the rescuer in undue danger. Ethical considerations also strongly support rendering aid. The principle of beneficence (acting in the best interest of the patient) and non-maleficence (avoiding harm) are paramount. Promptly calling for professional medical help is the most effective way to ensure the individual receives appropriate care, while providing basic first aid can stabilize the situation until that help arrives. An incorrect approach of attempting advanced medical procedures without proper training or certification would be a significant ethical and regulatory failure. This could lead to further injury, exacerbate the existing condition, and potentially result in legal liability for practicing medicine without a license. It violates the principle of non-maleficence and exceeds the professional’s scope of practice as defined by aviation regulations and professional standards. Another incorrect approach of delaying or refusing to call for emergency medical services due to uncertainty or a desire to avoid inconvenience is a failure of the duty of care. This inaction could lead to a worse outcome for the individual and constitutes a breach of professional responsibility and ethical obligations. Regulations often require professionals to act reasonably and prudently in emergency situations, and failing to summon professional help when clearly needed is not reasonable or prudent. A third incorrect approach of providing only basic comfort measures without initiating emergency medical services, even if the condition appears serious, is also inadequate. While comfort is important, it does not address the underlying medical issue that requires professional intervention. This approach fails to meet the standard of care expected in an emergency and could result in a delayed diagnosis and treatment, leading to adverse consequences. The professional decision-making process in such situations should involve a rapid assessment of the situation, identification of immediate threats to life, prioritization of actions (e.g., ensuring safety, calling for help, administering first aid), and adherence to established protocols and training. Professionals must be aware of their limitations and the resources available to them, acting decisively and responsibly within those parameters.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires immediate decision-making under pressure, balancing the immediate need for medical assistance with the potential for further harm or legal ramifications. The professional’s duty of care extends to ensuring the well-being of individuals in their care, which includes responding appropriately to medical emergencies. The core of the challenge lies in understanding the scope of one’s responsibilities and the appropriate actions to take within the established regulatory framework, without overstepping professional boundaries or failing to provide necessary aid. The correct approach involves recognizing the severity of the situation, initiating immediate emergency medical services, and providing basic first aid within the limits of one’s training and competence. This aligns with the NBAA Professional Examinations’ emphasis on safety and responsible conduct. Regulatory frameworks, such as those governing aviation professionals, typically mandate a duty of care to assist in emergencies, provided it does not place the rescuer in undue danger. Ethical considerations also strongly support rendering aid. The principle of beneficence (acting in the best interest of the patient) and non-maleficence (avoiding harm) are paramount. Promptly calling for professional medical help is the most effective way to ensure the individual receives appropriate care, while providing basic first aid can stabilize the situation until that help arrives. An incorrect approach of attempting advanced medical procedures without proper training or certification would be a significant ethical and regulatory failure. This could lead to further injury, exacerbate the existing condition, and potentially result in legal liability for practicing medicine without a license. It violates the principle of non-maleficence and exceeds the professional’s scope of practice as defined by aviation regulations and professional standards. Another incorrect approach of delaying or refusing to call for emergency medical services due to uncertainty or a desire to avoid inconvenience is a failure of the duty of care. This inaction could lead to a worse outcome for the individual and constitutes a breach of professional responsibility and ethical obligations. Regulations often require professionals to act reasonably and prudently in emergency situations, and failing to summon professional help when clearly needed is not reasonable or prudent. A third incorrect approach of providing only basic comfort measures without initiating emergency medical services, even if the condition appears serious, is also inadequate. While comfort is important, it does not address the underlying medical issue that requires professional intervention. This approach fails to meet the standard of care expected in an emergency and could result in a delayed diagnosis and treatment, leading to adverse consequences. The professional decision-making process in such situations should involve a rapid assessment of the situation, identification of immediate threats to life, prioritization of actions (e.g., ensuring safety, calling for help, administering first aid), and adherence to established protocols and training. Professionals must be aware of their limitations and the resources available to them, acting decisively and responsibly within those parameters.
-
Question 22 of 30
22. Question
Implementation of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) related to aircraft maintenance procedures requires a national aviation authority to conduct a comprehensive evaluation. Which of the following approaches best ensures compliance and upholds aviation safety?
Correct
The implementation of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) within a national aviation regulatory framework presents a significant professional challenge. This challenge stems from the need to interpret and integrate global standards into a specific national context, ensuring both compliance with international obligations and the practical applicability within the domestic aviation system. Professionals must exercise careful judgment to balance the intent of ICAO SARPs with national operational realities, safety objectives, and economic considerations. The correct approach involves a thorough risk assessment that prioritizes the safety implications of non-compliance with ICAO SARPs. This approach recognizes that ICAO SARPs are developed based on extensive research and global experience to ensure a high level of aviation safety worldwide. A risk assessment focused on safety implications will identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities arising from deviations or non-implementation, allowing for the development of mitigation strategies that align with the spirit and intent of the SARPs. This aligns with the ethical obligation of aviation professionals to uphold the highest standards of safety and security, as mandated by international agreements and national legislation that often incorporates ICAO standards. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on the economic cost of implementation without a commensurate safety risk assessment is professionally unacceptable. This failure ignores the primary purpose of ICAO SARPs, which is to enhance global aviation safety. Prioritizing cost savings over potential safety compromises violates the fundamental ethical duty to protect passengers, crew, and the public. Such an approach risks creating a less safe aviation environment, potentially leading to accidents and significant reputational damage. Another incorrect approach that relies on a superficial review of ICAO SARPs without engaging with the underlying safety rationale is also professionally unsound. This method may lead to the adoption of practices that appear compliant on the surface but fail to address the actual safety risks the SARPs are designed to mitigate. This demonstrates a lack of due diligence and a failure to understand the critical importance of the safety principles embedded within the SARPs, potentially leading to a false sense of security and overlooking critical safety deficiencies. A professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a structured risk management framework. This framework should begin with a comprehensive understanding of the relevant ICAO SARPs and their objectives. Subsequently, a detailed assessment of the potential safety, security, and operational impacts of implementing or not implementing these SARPs within the national context must be conducted. This assessment should involve relevant stakeholders and subject matter experts. Mitigation strategies should then be developed and implemented, with a continuous monitoring and evaluation process to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness. The ultimate goal is to achieve a level of safety that is at least equivalent to, if not exceeding, the intent of the ICAO SARPs, while considering national specificities.
Incorrect
The implementation of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) within a national aviation regulatory framework presents a significant professional challenge. This challenge stems from the need to interpret and integrate global standards into a specific national context, ensuring both compliance with international obligations and the practical applicability within the domestic aviation system. Professionals must exercise careful judgment to balance the intent of ICAO SARPs with national operational realities, safety objectives, and economic considerations. The correct approach involves a thorough risk assessment that prioritizes the safety implications of non-compliance with ICAO SARPs. This approach recognizes that ICAO SARPs are developed based on extensive research and global experience to ensure a high level of aviation safety worldwide. A risk assessment focused on safety implications will identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities arising from deviations or non-implementation, allowing for the development of mitigation strategies that align with the spirit and intent of the SARPs. This aligns with the ethical obligation of aviation professionals to uphold the highest standards of safety and security, as mandated by international agreements and national legislation that often incorporates ICAO standards. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on the economic cost of implementation without a commensurate safety risk assessment is professionally unacceptable. This failure ignores the primary purpose of ICAO SARPs, which is to enhance global aviation safety. Prioritizing cost savings over potential safety compromises violates the fundamental ethical duty to protect passengers, crew, and the public. Such an approach risks creating a less safe aviation environment, potentially leading to accidents and significant reputational damage. Another incorrect approach that relies on a superficial review of ICAO SARPs without engaging with the underlying safety rationale is also professionally unsound. This method may lead to the adoption of practices that appear compliant on the surface but fail to address the actual safety risks the SARPs are designed to mitigate. This demonstrates a lack of due diligence and a failure to understand the critical importance of the safety principles embedded within the SARPs, potentially leading to a false sense of security and overlooking critical safety deficiencies. A professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a structured risk management framework. This framework should begin with a comprehensive understanding of the relevant ICAO SARPs and their objectives. Subsequently, a detailed assessment of the potential safety, security, and operational impacts of implementing or not implementing these SARPs within the national context must be conducted. This assessment should involve relevant stakeholders and subject matter experts. Mitigation strategies should then be developed and implemented, with a continuous monitoring and evaluation process to ensure ongoing compliance and effectiveness. The ultimate goal is to achieve a level of safety that is at least equivalent to, if not exceeding, the intent of the ICAO SARPs, while considering national specificities.
-
Question 23 of 30
23. Question
Risk assessment procedures indicate that a flight department is experiencing inefficiencies in its flight planning and tracking processes due to outdated manual systems. A new software solution has been identified that promises to automate these functions, improve real-time data access for pilots and management, and potentially reduce operational costs. Considering the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus, which of the following represents the most appropriate approach to address this situation?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires an individual to navigate the complex requirements of the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus, specifically concerning the application of knowledge in a practical context. The challenge lies in accurately identifying which syllabus area is most relevant to a given situation and then applying the principles associated with that area. Careful judgment is required to distinguish between closely related concepts and to ensure that the chosen approach aligns with the overarching objectives of professional aviation management as outlined in the syllabus. The correct approach involves a thorough understanding of the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus and its emphasis on operational efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance. It requires recognizing that the scenario directly relates to the syllabus’s coverage of flight department management, specifically the integration of technology for operational improvement. This approach is correct because it demonstrates an ability to apply syllabus knowledge to a real-world problem, focusing on a solution that enhances operational effectiveness and aligns with best practices in aviation management. The NBAA syllabus prioritizes practical application of knowledge, and this approach directly addresses that. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on the technical aspects of the new software without considering its integration into the broader operational framework fails to meet the syllabus requirements. This is professionally unacceptable because it neglects the holistic management principles emphasized in the syllabus, which extend beyond mere technical implementation to encompass operational impact, cost-effectiveness, and crew training. Another incorrect approach that prioritizes immediate cost savings by delaying the implementation of the software, despite its potential for long-term efficiency gains, is also professionally flawed. This demonstrates a lack of strategic thinking and an inability to balance short-term financial considerations with the long-term operational benefits and competitive advantages that the syllabus encourages professionals to pursue. A further incorrect approach that involves implementing the software without adequate crew training or procedural updates ignores the critical human factors and safety elements that are integral to the NBAA syllabus. This oversight can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased risk, and non-compliance, all of which are contrary to the professional standards expected of individuals who have passed the NBAA Professional Examinations. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a systematic review of the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus to identify the most relevant sections. This should be followed by an analysis of the situation to determine how the principles and knowledge outlined in the syllabus can be applied to achieve the desired outcomes. Professionals should consider the operational, safety, regulatory, and financial implications of any proposed solution, always prioritizing alignment with the syllabus’s core tenets of effective and responsible aviation management.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires an individual to navigate the complex requirements of the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus, specifically concerning the application of knowledge in a practical context. The challenge lies in accurately identifying which syllabus area is most relevant to a given situation and then applying the principles associated with that area. Careful judgment is required to distinguish between closely related concepts and to ensure that the chosen approach aligns with the overarching objectives of professional aviation management as outlined in the syllabus. The correct approach involves a thorough understanding of the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus and its emphasis on operational efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance. It requires recognizing that the scenario directly relates to the syllabus’s coverage of flight department management, specifically the integration of technology for operational improvement. This approach is correct because it demonstrates an ability to apply syllabus knowledge to a real-world problem, focusing on a solution that enhances operational effectiveness and aligns with best practices in aviation management. The NBAA syllabus prioritizes practical application of knowledge, and this approach directly addresses that. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on the technical aspects of the new software without considering its integration into the broader operational framework fails to meet the syllabus requirements. This is professionally unacceptable because it neglects the holistic management principles emphasized in the syllabus, which extend beyond mere technical implementation to encompass operational impact, cost-effectiveness, and crew training. Another incorrect approach that prioritizes immediate cost savings by delaying the implementation of the software, despite its potential for long-term efficiency gains, is also professionally flawed. This demonstrates a lack of strategic thinking and an inability to balance short-term financial considerations with the long-term operational benefits and competitive advantages that the syllabus encourages professionals to pursue. A further incorrect approach that involves implementing the software without adequate crew training or procedural updates ignores the critical human factors and safety elements that are integral to the NBAA syllabus. This oversight can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased risk, and non-compliance, all of which are contrary to the professional standards expected of individuals who have passed the NBAA Professional Examinations. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a systematic review of the NBAA Professional Examinations syllabus to identify the most relevant sections. This should be followed by an analysis of the situation to determine how the principles and knowledge outlined in the syllabus can be applied to achieve the desired outcomes. Professionals should consider the operational, safety, regulatory, and financial implications of any proposed solution, always prioritizing alignment with the syllabus’s core tenets of effective and responsible aviation management.
-
Question 24 of 30
24. Question
Investigation of a pilot’s report detailing an unusual vibration during climb, which the line maintenance technician initially attributed to normal engine operation without further inspection, presents a critical juncture. What is the most appropriate immediate course of action for the responsible aviation professional to assess potential liability and negligence?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a nuanced understanding of an aviation professional’s duty of care and the potential for negligence in the context of aircraft maintenance. The core difficulty lies in distinguishing between a minor, unavoidable issue and a failure to exercise reasonable care that could lead to harm. Professionals must balance operational efficiency with an unwavering commitment to safety, adhering strictly to the regulatory framework governing aviation maintenance. The correct approach involves a thorough, documented investigation into the reported issue, including a comprehensive review of maintenance logs, the specific component’s history, and the applicable maintenance manual procedures. This approach is right because it directly addresses the potential for negligence by systematically gathering evidence to determine if a breach of the standard of care occurred. The NBAA Professional Examinations, by extension, would expect adherence to the principles of due diligence and the regulatory requirements for record-keeping and maintenance oversight, which are paramount in preventing accidents and ensuring passenger safety. This systematic investigation aligns with the overarching goal of aviation safety regulations to ensure that all maintenance is performed to the highest standards. An incorrect approach would be to dismiss the report without further investigation, assuming it is a minor issue. This fails to meet the standard of care expected of aviation professionals. The regulatory framework mandates that all reported discrepancies, regardless of perceived severity, must be investigated to ensure airworthiness. This dismissive attitude could lead to a failure to identify a latent defect, thereby breaching the duty of care and potentially leading to a catastrophic event, which is a direct violation of safety regulations and ethical obligations. Another incorrect approach would be to perform a superficial check and immediately sign off on the aircraft’s airworthiness without proper documentation or consultation with relevant technical experts or manufacturers. This bypasses critical safety protocols and demonstrates a lack of due diligence. The regulatory framework emphasizes meticulous record-keeping and adherence to approved maintenance data. Failing to follow these procedures constitutes negligence, as it undermines the integrity of the maintenance process and the safety assurance system. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a structured approach: 1. Acknowledge and document the reported issue immediately. 2. Consult relevant maintenance manuals, service bulletins, and manufacturer recommendations. 3. Conduct a thorough inspection and diagnostic testing as required. 4. Document all findings, actions taken, and the rationale behind them. 5. If necessary, consult with senior maintenance personnel, technical specialists, or the aircraft manufacturer. 6. Ensure all actions taken are in compliance with applicable regulations and approved data before releasing the aircraft for service. This methodical process ensures that safety is prioritized and that all actions are defensible from a regulatory and ethical standpoint.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a nuanced understanding of an aviation professional’s duty of care and the potential for negligence in the context of aircraft maintenance. The core difficulty lies in distinguishing between a minor, unavoidable issue and a failure to exercise reasonable care that could lead to harm. Professionals must balance operational efficiency with an unwavering commitment to safety, adhering strictly to the regulatory framework governing aviation maintenance. The correct approach involves a thorough, documented investigation into the reported issue, including a comprehensive review of maintenance logs, the specific component’s history, and the applicable maintenance manual procedures. This approach is right because it directly addresses the potential for negligence by systematically gathering evidence to determine if a breach of the standard of care occurred. The NBAA Professional Examinations, by extension, would expect adherence to the principles of due diligence and the regulatory requirements for record-keeping and maintenance oversight, which are paramount in preventing accidents and ensuring passenger safety. This systematic investigation aligns with the overarching goal of aviation safety regulations to ensure that all maintenance is performed to the highest standards. An incorrect approach would be to dismiss the report without further investigation, assuming it is a minor issue. This fails to meet the standard of care expected of aviation professionals. The regulatory framework mandates that all reported discrepancies, regardless of perceived severity, must be investigated to ensure airworthiness. This dismissive attitude could lead to a failure to identify a latent defect, thereby breaching the duty of care and potentially leading to a catastrophic event, which is a direct violation of safety regulations and ethical obligations. Another incorrect approach would be to perform a superficial check and immediately sign off on the aircraft’s airworthiness without proper documentation or consultation with relevant technical experts or manufacturers. This bypasses critical safety protocols and demonstrates a lack of due diligence. The regulatory framework emphasizes meticulous record-keeping and adherence to approved maintenance data. Failing to follow these procedures constitutes negligence, as it undermines the integrity of the maintenance process and the safety assurance system. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a structured approach: 1. Acknowledge and document the reported issue immediately. 2. Consult relevant maintenance manuals, service bulletins, and manufacturer recommendations. 3. Conduct a thorough inspection and diagnostic testing as required. 4. Document all findings, actions taken, and the rationale behind them. 5. If necessary, consult with senior maintenance personnel, technical specialists, or the aircraft manufacturer. 6. Ensure all actions taken are in compliance with applicable regulations and approved data before releasing the aircraft for service. This methodical process ensures that safety is prioritized and that all actions are defensible from a regulatory and ethical standpoint.
-
Question 25 of 30
25. Question
Performance analysis shows a consistent decline in the proactive reporting of minor operational discrepancies by a flight operations team over the past quarter. Team members appear less engaged during pre-flight briefings, and there’s a noticeable increase in instances where standard operating procedures are followed with minimal initiative. The team leader, while experienced, has primarily focused on ensuring task completion rather than fostering team cohesion or addressing individual concerns. What is the most appropriate course of action for the team leader to address this situation?
Correct
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires balancing the need for immediate operational efficiency with the long-term strategic imperative of fostering a motivated and cohesive team. The aviation industry, particularly within the context of NBAA Professional Examinations, emphasizes safety, compliance, and operational excellence, all of which are significantly influenced by team dynamics and individual motivation. A failure to address underlying motivational issues can lead to decreased performance, increased errors, and potential safety compromises, which are unacceptable in this regulated environment. Careful judgment is required to identify the root causes of demotivation and implement solutions that are both effective and compliant with industry standards. The correct approach involves a proactive and empathetic engagement with the team to understand the specific factors contributing to their reduced motivation. This includes open communication, active listening, and a willingness to address concerns directly. By seeking to understand individual and collective needs, a leader can then implement tailored strategies, such as providing clear goals, recognizing contributions, fostering a supportive work environment, and offering opportunities for professional development. This approach aligns with ethical principles of leadership that prioritize employee well-being and engagement, and indirectly supports regulatory compliance by promoting a culture of diligence and attention to detail, which are paramount in aviation operations. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on increased oversight and punitive measures fails to address the underlying causes of demotivation. This can exacerbate the problem by creating a climate of fear and distrust, leading to further disengagement and potentially masking deeper systemic issues. Such an approach is ethically questionable as it disregards the human element of the workforce and can lead to a breakdown in communication, hindering the identification and resolution of operational problems. Another incorrect approach that involves superficial team-building activities without addressing core issues is also professionally unacceptable. While team-building can be beneficial, it is ineffective if it does not tackle the root causes of low morale. This approach can be seen as a failure to exercise due diligence in leadership, as it avoids confronting difficult but necessary conversations and actions. It also risks being perceived as insincere by the team, further eroding trust. A professional decision-making process for similar situations should begin with a thorough assessment of the situation, gathering data and feedback from multiple sources. This should be followed by an analysis of potential root causes, considering both individual and systemic factors. Solutions should then be developed collaboratively with the team where appropriate, prioritizing interventions that are ethical, sustainable, and aligned with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. Continuous monitoring and feedback are essential to ensure the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
Incorrect
This scenario presents a professional challenge because it requires balancing the need for immediate operational efficiency with the long-term strategic imperative of fostering a motivated and cohesive team. The aviation industry, particularly within the context of NBAA Professional Examinations, emphasizes safety, compliance, and operational excellence, all of which are significantly influenced by team dynamics and individual motivation. A failure to address underlying motivational issues can lead to decreased performance, increased errors, and potential safety compromises, which are unacceptable in this regulated environment. Careful judgment is required to identify the root causes of demotivation and implement solutions that are both effective and compliant with industry standards. The correct approach involves a proactive and empathetic engagement with the team to understand the specific factors contributing to their reduced motivation. This includes open communication, active listening, and a willingness to address concerns directly. By seeking to understand individual and collective needs, a leader can then implement tailored strategies, such as providing clear goals, recognizing contributions, fostering a supportive work environment, and offering opportunities for professional development. This approach aligns with ethical principles of leadership that prioritize employee well-being and engagement, and indirectly supports regulatory compliance by promoting a culture of diligence and attention to detail, which are paramount in aviation operations. An incorrect approach that focuses solely on increased oversight and punitive measures fails to address the underlying causes of demotivation. This can exacerbate the problem by creating a climate of fear and distrust, leading to further disengagement and potentially masking deeper systemic issues. Such an approach is ethically questionable as it disregards the human element of the workforce and can lead to a breakdown in communication, hindering the identification and resolution of operational problems. Another incorrect approach that involves superficial team-building activities without addressing core issues is also professionally unacceptable. While team-building can be beneficial, it is ineffective if it does not tackle the root causes of low morale. This approach can be seen as a failure to exercise due diligence in leadership, as it avoids confronting difficult but necessary conversations and actions. It also risks being perceived as insincere by the team, further eroding trust. A professional decision-making process for similar situations should begin with a thorough assessment of the situation, gathering data and feedback from multiple sources. This should be followed by an analysis of potential root causes, considering both individual and systemic factors. Solutions should then be developed collaboratively with the team where appropriate, prioritizing interventions that are ethical, sustainable, and aligned with organizational goals and regulatory requirements. Continuous monitoring and feedback are essential to ensure the effectiveness of implemented strategies.
-
Question 26 of 30
26. Question
To address the challenge of a flight encountering unexpected headwinds that are depleting fuel reserves faster than anticipated, and with the destination weather forecast to be at minimums upon estimated arrival, what is the most prudent course of action for the pilot to ensure the safety of the flight?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a pilot to balance operational efficiency and safety with regulatory compliance, especially when faced with potential fuel shortages. The pilot must make a critical decision that directly impacts the safety of the flight and the well-being of passengers and crew. The decision-making process must be grounded in established aviation regulations and best practices for fuel management. The correct approach involves a thorough assessment of available fuel against the planned flight requirements, including contingency fuel, and making a proactive decision to divert if the fuel situation becomes marginal. This aligns with the fundamental principle of aviation safety, which mandates that pilots must not operate an aircraft in a manner that endangers it or any person on board. Specifically, regulations like those found in the NBAA Professional Examinations framework (which would mirror FAA regulations in the US context for Part 91 operations) require pilots to ensure sufficient fuel for the flight, including reserves. The decision to divert before reaching a critical fuel state is a proactive safety measure that prevents a potential emergency landing due to fuel exhaustion. This demonstrates sound judgment and adherence to the highest safety standards. An incorrect approach would be to continue the flight with the hope of reaching the destination, despite a known fuel shortage and insufficient reserves. This directly violates the regulatory requirement to carry adequate fuel and reserves. It prioritizes expediency over safety and exposes the aircraft and its occupants to an unacceptable risk of fuel exhaustion, which could lead to a forced landing or crash. Another incorrect approach would be to rely solely on the hope that weather conditions at the destination will improve sufficiently to allow for a landing without requiring additional fuel for holding or diversions, without a concrete plan or sufficient fuel to accommodate potential delays. This is a speculative approach that disregards the need for concrete fuel planning and contingency measures. Finally, an incorrect approach would be to request an expedited clearance to the destination without a corresponding increase in fuel planning or a clear understanding of the fuel remaining upon arrival, potentially leading to a rushed and unsafe decision-making process. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that prioritizes safety above all else. This involves a systematic evaluation of the situation, considering all available data (fuel status, weather, flight plan, aircraft performance), and consulting relevant regulations and company policies. When faced with uncertainty or a deviation from the planned flight, the framework should guide the pilot to err on the side of caution, making proactive decisions that mitigate risk. This includes having a clear understanding of minimum fuel requirements and contingency plans, and being prepared to divert to an alternate airport if necessary, even if it causes inconvenience.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a pilot to balance operational efficiency and safety with regulatory compliance, especially when faced with potential fuel shortages. The pilot must make a critical decision that directly impacts the safety of the flight and the well-being of passengers and crew. The decision-making process must be grounded in established aviation regulations and best practices for fuel management. The correct approach involves a thorough assessment of available fuel against the planned flight requirements, including contingency fuel, and making a proactive decision to divert if the fuel situation becomes marginal. This aligns with the fundamental principle of aviation safety, which mandates that pilots must not operate an aircraft in a manner that endangers it or any person on board. Specifically, regulations like those found in the NBAA Professional Examinations framework (which would mirror FAA regulations in the US context for Part 91 operations) require pilots to ensure sufficient fuel for the flight, including reserves. The decision to divert before reaching a critical fuel state is a proactive safety measure that prevents a potential emergency landing due to fuel exhaustion. This demonstrates sound judgment and adherence to the highest safety standards. An incorrect approach would be to continue the flight with the hope of reaching the destination, despite a known fuel shortage and insufficient reserves. This directly violates the regulatory requirement to carry adequate fuel and reserves. It prioritizes expediency over safety and exposes the aircraft and its occupants to an unacceptable risk of fuel exhaustion, which could lead to a forced landing or crash. Another incorrect approach would be to rely solely on the hope that weather conditions at the destination will improve sufficiently to allow for a landing without requiring additional fuel for holding or diversions, without a concrete plan or sufficient fuel to accommodate potential delays. This is a speculative approach that disregards the need for concrete fuel planning and contingency measures. Finally, an incorrect approach would be to request an expedited clearance to the destination without a corresponding increase in fuel planning or a clear understanding of the fuel remaining upon arrival, potentially leading to a rushed and unsafe decision-making process. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that prioritizes safety above all else. This involves a systematic evaluation of the situation, considering all available data (fuel status, weather, flight plan, aircraft performance), and consulting relevant regulations and company policies. When faced with uncertainty or a deviation from the planned flight, the framework should guide the pilot to err on the side of caution, making proactive decisions that mitigate risk. This includes having a clear understanding of minimum fuel requirements and contingency plans, and being prepared to divert to an alternate airport if necessary, even if it causes inconvenience.
-
Question 27 of 30
27. Question
When evaluating a situation where an unusual and potentially concerning smell is detected in the cabin during cruise flight, and the flight crew suspects a possible electrical issue, what is the most appropriate immediate course of action according to standard aviation emergency response planning principles?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires immediate, decisive action under pressure, balancing the safety of individuals with the operational continuity of the aircraft and the potential for regulatory scrutiny. The complexity arises from the need to assess a rapidly evolving situation, communicate effectively with all relevant parties, and make decisions that align with established emergency response protocols and regulatory mandates. The pilot’s judgment is paramount in determining the appropriate course of action, which must be both safe and compliant. The correct approach involves a systematic assessment of the situation, prioritizing immediate safety, and then executing the pre-defined emergency response plan. This includes informing the appropriate authorities and passengers as per established procedures. This approach is correct because it directly adheres to the fundamental principles of aviation safety and emergency management, which are codified in regulations designed to protect lives and mitigate risks. Specifically, it aligns with the regulatory framework’s emphasis on pilot-in-command authority and responsibility for the safe operation of the aircraft, including the implementation of emergency procedures. Ethical considerations also dictate that the well-being of passengers and crew is the highest priority. An incorrect approach would be to delay reporting the issue to the relevant authorities, hoping it resolves itself. This fails to acknowledge the potential for escalation and the regulatory requirement for timely notification of significant events. It also bypasses established communication protocols designed to ensure a coordinated response. Another incorrect approach would be to attempt a complex, unverified fix without consulting available resources or adhering to established emergency checklists. This introduces unnecessary risk and deviates from the principle of following approved procedures during emergencies. Finally, an approach that prioritizes avoiding operational disruption over passenger safety, such as continuing the flight without proper assessment or communication, is a severe regulatory and ethical failure. It demonstrates a disregard for the pilot’s primary duty of care and the stringent safety standards mandated by aviation authorities. Professional decision-making in such situations requires a clear understanding of the aircraft’s emergency procedures, a thorough knowledge of regulatory requirements for reporting and handling emergencies, and the ability to remain calm and analytical under stress. The process involves: 1) immediate threat assessment, 2) adherence to established checklists and procedures, 3) clear and concise communication with the flight crew and air traffic control, 4) informed decision-making regarding diversion or continuation, and 5) post-incident reporting and follow-up as required by regulations.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires immediate, decisive action under pressure, balancing the safety of individuals with the operational continuity of the aircraft and the potential for regulatory scrutiny. The complexity arises from the need to assess a rapidly evolving situation, communicate effectively with all relevant parties, and make decisions that align with established emergency response protocols and regulatory mandates. The pilot’s judgment is paramount in determining the appropriate course of action, which must be both safe and compliant. The correct approach involves a systematic assessment of the situation, prioritizing immediate safety, and then executing the pre-defined emergency response plan. This includes informing the appropriate authorities and passengers as per established procedures. This approach is correct because it directly adheres to the fundamental principles of aviation safety and emergency management, which are codified in regulations designed to protect lives and mitigate risks. Specifically, it aligns with the regulatory framework’s emphasis on pilot-in-command authority and responsibility for the safe operation of the aircraft, including the implementation of emergency procedures. Ethical considerations also dictate that the well-being of passengers and crew is the highest priority. An incorrect approach would be to delay reporting the issue to the relevant authorities, hoping it resolves itself. This fails to acknowledge the potential for escalation and the regulatory requirement for timely notification of significant events. It also bypasses established communication protocols designed to ensure a coordinated response. Another incorrect approach would be to attempt a complex, unverified fix without consulting available resources or adhering to established emergency checklists. This introduces unnecessary risk and deviates from the principle of following approved procedures during emergencies. Finally, an approach that prioritizes avoiding operational disruption over passenger safety, such as continuing the flight without proper assessment or communication, is a severe regulatory and ethical failure. It demonstrates a disregard for the pilot’s primary duty of care and the stringent safety standards mandated by aviation authorities. Professional decision-making in such situations requires a clear understanding of the aircraft’s emergency procedures, a thorough knowledge of regulatory requirements for reporting and handling emergencies, and the ability to remain calm and analytical under stress. The process involves: 1) immediate threat assessment, 2) adherence to established checklists and procedures, 3) clear and concise communication with the flight crew and air traffic control, 4) informed decision-making regarding diversion or continuation, and 5) post-incident reporting and follow-up as required by regulations.
-
Question 28 of 30
28. Question
The performance metrics show a significant decline in productivity and an increase in access to sensitive data outside of normal working hours for a specific employee. What is the most appropriate initial course of action to mitigate a potential insider threat?
Correct
Scenario Analysis: This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires balancing the need for robust insider threat mitigation with the protection of employee privacy and the avoidance of creating a climate of distrust. The performance metrics, while potentially indicative of a problem, are not definitive proof of malicious intent. Acting too aggressively based solely on these metrics could lead to unfair accusations, damage morale, and potentially violate privacy regulations. Conversely, ignoring concerning trends could expose the organization to significant risks. Careful judgment is required to investigate discreetly and ethically, ensuring that any actions taken are proportionate, justified, and compliant with all applicable regulations. Correct Approach Analysis: The correct approach involves initiating a discreet, multi-disciplinary internal investigation. This approach is right because it prioritizes a thorough, fact-based assessment before any punitive or corrective actions are taken. It involves gathering additional, corroborating evidence through channels that respect privacy and adhere to established company policies and legal frameworks. This might include reviewing access logs, communication patterns (within legal and policy limits), and other relevant data points that can provide context without being overly intrusive. The goal is to determine if there is a genuine insider threat and, if so, to understand its nature and scope. This aligns with the ethical obligation to treat employees fairly and the regulatory requirement to have a well-founded basis for any disciplinary actions or security enhancements. It also supports the principle of proportionality in security measures. Incorrect Approaches Analysis: Immediately confronting the employee based solely on performance metrics is an incorrect approach. This fails to acknowledge that performance metrics can be influenced by various factors unrelated to malicious intent, such as training needs, workload issues, or personal circumstances. Such a confrontation without further evidence could lead to wrongful accusations, damage the employee’s reputation and career, and create significant legal and HR liabilities for the organization. It also bypasses the necessary due diligence required in investigating potential security threats. Implementing broad, intrusive surveillance measures across the entire workforce without specific cause is another incorrect approach. While it might seem like a proactive step, it is overly punitive, likely to violate employee privacy rights and data protection regulations, and can severely damage employee morale and trust. Such measures are generally not justifiable based on isolated performance metrics and would likely be seen as a disproportionate response, potentially leading to legal challenges and a negative organizational culture. Escalating the issue to external law enforcement immediately without internal investigation is also an incorrect approach. While external involvement may be necessary in certain severe cases, it should be a last resort after internal assessment has established a credible and significant threat. Prematurely involving law enforcement can have severe consequences for the employee’s life and liberty, and can also damage the organization’s reputation and create unnecessary legal complexities if the initial assessment proves to be unfounded. It bypasses the organization’s responsibility to conduct its own due diligence and manage its internal security matters appropriately. Professional Reasoning: Professionals should employ a structured decision-making framework that begins with objective data assessment. When concerning data emerges, the next step is to consider potential causes, distinguishing between benign and malicious explanations. A discreet, evidence-gathering phase, guided by company policy and legal counsel, is crucial. This phase should focus on corroborating the initial concerns with more direct evidence of malicious intent or policy violation, while respecting privacy. Only after a credible threat is established should proportionate actions, such as targeted investigation, employee interviews (with appropriate representation), or enhanced security controls, be considered. If the evidence points to criminal activity, then escalation to external authorities becomes appropriate, but this decision must be informed by the findings of the internal investigation.
Incorrect
Scenario Analysis: This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires balancing the need for robust insider threat mitigation with the protection of employee privacy and the avoidance of creating a climate of distrust. The performance metrics, while potentially indicative of a problem, are not definitive proof of malicious intent. Acting too aggressively based solely on these metrics could lead to unfair accusations, damage morale, and potentially violate privacy regulations. Conversely, ignoring concerning trends could expose the organization to significant risks. Careful judgment is required to investigate discreetly and ethically, ensuring that any actions taken are proportionate, justified, and compliant with all applicable regulations. Correct Approach Analysis: The correct approach involves initiating a discreet, multi-disciplinary internal investigation. This approach is right because it prioritizes a thorough, fact-based assessment before any punitive or corrective actions are taken. It involves gathering additional, corroborating evidence through channels that respect privacy and adhere to established company policies and legal frameworks. This might include reviewing access logs, communication patterns (within legal and policy limits), and other relevant data points that can provide context without being overly intrusive. The goal is to determine if there is a genuine insider threat and, if so, to understand its nature and scope. This aligns with the ethical obligation to treat employees fairly and the regulatory requirement to have a well-founded basis for any disciplinary actions or security enhancements. It also supports the principle of proportionality in security measures. Incorrect Approaches Analysis: Immediately confronting the employee based solely on performance metrics is an incorrect approach. This fails to acknowledge that performance metrics can be influenced by various factors unrelated to malicious intent, such as training needs, workload issues, or personal circumstances. Such a confrontation without further evidence could lead to wrongful accusations, damage the employee’s reputation and career, and create significant legal and HR liabilities for the organization. It also bypasses the necessary due diligence required in investigating potential security threats. Implementing broad, intrusive surveillance measures across the entire workforce without specific cause is another incorrect approach. While it might seem like a proactive step, it is overly punitive, likely to violate employee privacy rights and data protection regulations, and can severely damage employee morale and trust. Such measures are generally not justifiable based on isolated performance metrics and would likely be seen as a disproportionate response, potentially leading to legal challenges and a negative organizational culture. Escalating the issue to external law enforcement immediately without internal investigation is also an incorrect approach. While external involvement may be necessary in certain severe cases, it should be a last resort after internal assessment has established a credible and significant threat. Prematurely involving law enforcement can have severe consequences for the employee’s life and liberty, and can also damage the organization’s reputation and create unnecessary legal complexities if the initial assessment proves to be unfounded. It bypasses the organization’s responsibility to conduct its own due diligence and manage its internal security matters appropriately. Professional Reasoning: Professionals should employ a structured decision-making framework that begins with objective data assessment. When concerning data emerges, the next step is to consider potential causes, distinguishing between benign and malicious explanations. A discreet, evidence-gathering phase, guided by company policy and legal counsel, is crucial. This phase should focus on corroborating the initial concerns with more direct evidence of malicious intent or policy violation, while respecting privacy. Only after a credible threat is established should proportionate actions, such as targeted investigation, employee interviews (with appropriate representation), or enhanced security controls, be considered. If the evidence points to criminal activity, then escalation to external authorities becomes appropriate, but this decision must be informed by the findings of the internal investigation.
-
Question 29 of 30
29. Question
Upon reviewing the established compliance program for a business aviation operation, what is the most effective and regulatory-compliant method to assess its ongoing effectiveness and identify potential areas for improvement?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a nuanced understanding of the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework concerning compliance programs and auditing. The challenge lies in identifying the most effective and compliant method for assessing the effectiveness of a compliance program, balancing thoroughness with practicality. Careful judgment is required to ensure that the chosen approach aligns with the spirit and letter of NBAA guidelines, which emphasize proactive risk management and continuous improvement. The correct approach involves a comprehensive, risk-based audit that goes beyond mere documentation review. This method is right because it directly addresses the core purpose of a compliance audit: to verify that the compliance program is not only in place but also functioning effectively in practice. A risk-based audit prioritizes areas of highest potential non-compliance, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and that the most critical aspects of the program are rigorously tested. This aligns with regulatory expectations for robust compliance oversight and demonstrates a commitment to identifying and mitigating potential violations before they occur. An approach that focuses solely on reviewing documented policies and procedures is professionally unacceptable because it fails to assess the actual implementation and effectiveness of those policies. Regulations and guidelines often require demonstrable evidence of compliance, not just the existence of written rules. This approach risks overlooking gaps where policies are not being followed in practice, leading to potential non-compliance. Another incorrect approach, relying exclusively on self-assessments without independent verification, is also professionally flawed. While self-assessments can be a useful component of a compliance program, they lack the objectivity and independence necessary for a truly effective audit. This can lead to a biased view of the program’s effectiveness and may fail to identify systemic issues that internal personnel might overlook or downplay. Finally, an approach that only audits compliance in response to specific incidents or complaints is insufficient. While reactive measures are important, a proactive and systematic audit process is essential for a comprehensive compliance program. Waiting for problems to arise before auditing means that potential risks may have already materialized, leading to regulatory penalties or reputational damage. Effective compliance auditing requires regular, scheduled reviews to ensure ongoing adherence to standards. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with understanding the specific regulatory requirements of the NBAA Professional Examinations. This involves identifying the objectives of the compliance program and the potential risks associated with its operations. The next step is to design an audit methodology that is risk-based, comprehensive, and includes both documentation review and practical testing of controls. Regular evaluation and adaptation of the audit process based on findings and evolving risks are crucial for maintaining an effective compliance program.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires a nuanced understanding of the NBAA Professional Examinations’ regulatory framework concerning compliance programs and auditing. The challenge lies in identifying the most effective and compliant method for assessing the effectiveness of a compliance program, balancing thoroughness with practicality. Careful judgment is required to ensure that the chosen approach aligns with the spirit and letter of NBAA guidelines, which emphasize proactive risk management and continuous improvement. The correct approach involves a comprehensive, risk-based audit that goes beyond mere documentation review. This method is right because it directly addresses the core purpose of a compliance audit: to verify that the compliance program is not only in place but also functioning effectively in practice. A risk-based audit prioritizes areas of highest potential non-compliance, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and that the most critical aspects of the program are rigorously tested. This aligns with regulatory expectations for robust compliance oversight and demonstrates a commitment to identifying and mitigating potential violations before they occur. An approach that focuses solely on reviewing documented policies and procedures is professionally unacceptable because it fails to assess the actual implementation and effectiveness of those policies. Regulations and guidelines often require demonstrable evidence of compliance, not just the existence of written rules. This approach risks overlooking gaps where policies are not being followed in practice, leading to potential non-compliance. Another incorrect approach, relying exclusively on self-assessments without independent verification, is also professionally flawed. While self-assessments can be a useful component of a compliance program, they lack the objectivity and independence necessary for a truly effective audit. This can lead to a biased view of the program’s effectiveness and may fail to identify systemic issues that internal personnel might overlook or downplay. Finally, an approach that only audits compliance in response to specific incidents or complaints is insufficient. While reactive measures are important, a proactive and systematic audit process is essential for a comprehensive compliance program. Waiting for problems to arise before auditing means that potential risks may have already materialized, leading to regulatory penalties or reputational damage. Effective compliance auditing requires regular, scheduled reviews to ensure ongoing adherence to standards. Professionals should employ a decision-making framework that begins with understanding the specific regulatory requirements of the NBAA Professional Examinations. This involves identifying the objectives of the compliance program and the potential risks associated with its operations. The next step is to design an audit methodology that is risk-based, comprehensive, and includes both documentation review and practical testing of controls. Regular evaluation and adaptation of the audit process based on findings and evolving risks are crucial for maintaining an effective compliance program.
-
Question 30 of 30
30. Question
Which approach would be most effective in optimizing the customs and immigration clearance process for a fleet of international business jets operating into the United States, considering the need to minimize ground time while ensuring full compliance with CBP and TSA regulations?
Correct
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires balancing operational efficiency with strict adherence to customs and immigration regulations, which are critical for maintaining compliance and avoiding significant penalties. The core challenge lies in optimizing the process of clearing aircraft and passengers through customs and immigration while ensuring all legal requirements are met without causing undue delays. This requires a nuanced understanding of both the regulatory framework and the practicalities of aviation operations. The correct approach involves a proactive and integrated strategy that leverages technology and pre-clearance mechanisms. This method is professionally sound because it directly addresses the regulatory requirements for passenger and baggage screening, duty declarations, and immigration checks in a manner that minimizes disruption to flight schedules. By utilizing pre-arrival processing and digital submission of manifests and passenger data, operators can significantly expedite the physical clearance process upon arrival, thereby optimizing the flow of both people and goods. This aligns with the spirit of regulations designed to facilitate legitimate travel and trade while maintaining security and compliance. An incorrect approach that relies solely on manual processing and reactive measures fails to optimize the process. This method is professionally unacceptable because it is inherently inefficient and increases the risk of non-compliance. Manual data entry and on-site verification are prone to errors, delays, and can lead to backlogs, especially during peak travel times. Such an approach disregards the potential for technological solutions and proactive planning, which are essential for modern aviation operations and regulatory adherence. Another incorrect approach that focuses on cutting corners to save time, such as incomplete manifest submissions or bypassing certain screening protocols, is ethically and regulatorily disastrous. This demonstrates a severe lack of professional judgment and a disregard for the law. Such actions not only expose the operator to severe fines and legal repercussions but also compromise national security and public safety, which are paramount concerns for customs and immigration authorities. A further incorrect approach that prioritizes passenger convenience over regulatory compliance, for instance, by allowing passengers to bypass immigration checks under the guise of expediency, is equally flawed. While passenger experience is important, it must never supersede legal obligations. This approach demonstrates a fundamental misunderstanding of the purpose and authority of customs and immigration procedures. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a thorough understanding of the applicable customs and immigration laws and guidelines. Professionals must then assess the operational constraints and identify opportunities for process improvement that are compliant with these regulations. This often involves researching and implementing technological solutions, establishing clear communication channels with relevant authorities, and conducting regular training for staff on updated procedures. A risk-based approach, focusing on identifying potential bottlenecks and compliance gaps, is crucial for developing effective and sustainable solutions.
Incorrect
This scenario is professionally challenging because it requires balancing operational efficiency with strict adherence to customs and immigration regulations, which are critical for maintaining compliance and avoiding significant penalties. The core challenge lies in optimizing the process of clearing aircraft and passengers through customs and immigration while ensuring all legal requirements are met without causing undue delays. This requires a nuanced understanding of both the regulatory framework and the practicalities of aviation operations. The correct approach involves a proactive and integrated strategy that leverages technology and pre-clearance mechanisms. This method is professionally sound because it directly addresses the regulatory requirements for passenger and baggage screening, duty declarations, and immigration checks in a manner that minimizes disruption to flight schedules. By utilizing pre-arrival processing and digital submission of manifests and passenger data, operators can significantly expedite the physical clearance process upon arrival, thereby optimizing the flow of both people and goods. This aligns with the spirit of regulations designed to facilitate legitimate travel and trade while maintaining security and compliance. An incorrect approach that relies solely on manual processing and reactive measures fails to optimize the process. This method is professionally unacceptable because it is inherently inefficient and increases the risk of non-compliance. Manual data entry and on-site verification are prone to errors, delays, and can lead to backlogs, especially during peak travel times. Such an approach disregards the potential for technological solutions and proactive planning, which are essential for modern aviation operations and regulatory adherence. Another incorrect approach that focuses on cutting corners to save time, such as incomplete manifest submissions or bypassing certain screening protocols, is ethically and regulatorily disastrous. This demonstrates a severe lack of professional judgment and a disregard for the law. Such actions not only expose the operator to severe fines and legal repercussions but also compromise national security and public safety, which are paramount concerns for customs and immigration authorities. A further incorrect approach that prioritizes passenger convenience over regulatory compliance, for instance, by allowing passengers to bypass immigration checks under the guise of expediency, is equally flawed. While passenger experience is important, it must never supersede legal obligations. This approach demonstrates a fundamental misunderstanding of the purpose and authority of customs and immigration procedures. The professional decision-making process for similar situations should involve a thorough understanding of the applicable customs and immigration laws and guidelines. Professionals must then assess the operational constraints and identify opportunities for process improvement that are compliant with these regulations. This often involves researching and implementing technological solutions, establishing clear communication channels with relevant authorities, and conducting regular training for staff on updated procedures. A risk-based approach, focusing on identifying potential bottlenecks and compliance gaps, is crucial for developing effective and sustainable solutions.